Hello, friends. We really like Docker and Jenkins so I thought why not make a post about both? Yeah, that’s a good idea. So, in this post, you will learn how to run Jenkins with Docker Compose. The process is simple and quick to do.
Before we get started…
Jenkins is a Java-based tool used by DevOps in continuous integration. It is one of the most popular and important in the world and it is worth taking a look at it.
On the other hand, we have talked about Docker in this post, and in summary, we can say that it is a container technology that allows us to distribute images of applications that we can run on any system that supports Docker. Also, Docker is used for software distribution and that is why Jenkins can also be deployed on a server using this technology.
Install Docker
Before you start, you have to install Docker on the system. In our case, we have chosen Debian which is quite popular among developers.
So, to install Docker on Debian 11 and get it up and running, we recommend you to read our post
How to install Docker on Debian 11?
Thanks to this post, you will be able to get a recent version of Docker. This will allow Jenkins and all the images we can use, to run correctly and take full advantage of Docker.
After you have Docker installed, the next step is to install docker-compose.
sudo apt install docker-compose
Now you’re done. With both packages installed, we can continue.
Running Jenkins with Docker Compose
Create a folder called jenkins and inside it the file docker-compose.yml.
mkdir jenkins cd jenkins nano docker-compose.yml
And add the following content
version: '3.3'
services:
jenkins:
container_name: jenkins
restart: always
image: jenkins/jenkins:lts
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- jenkins-home:/var/jenkins_home
volumes:
jenkins-home:
Thanks to this file, we will be able to deploy the Jenkins image. This image is in Docker Hub and I will proceed quickly to explain it to you.
Version: '3.3' does not refer to the Jenkins or Docker version but to the YML version. We have named a service called jenkins which has the same name as the container but uses an image called jenkins-lts which as I said is on Docker Hub and uses the latest LTS version of Jenkins. The image that uses port 8080 will be redirected to port 8080 on our machine. Finally set up a volume so we can access the Jenkins data.
Save the changes and close the editor.
Now run the image with this command
docker-compose up -d
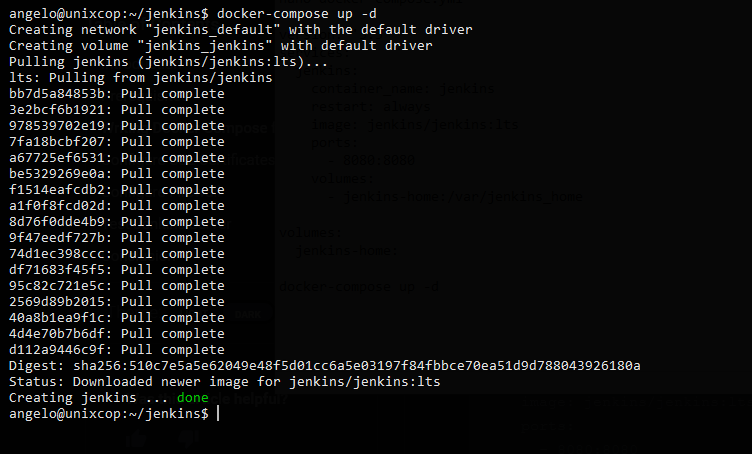
In the end, you will see an output screen indicating that the whole process has been successful.
Also, you can check this by running
docker-compose ps
Optional: Install Nginx as a reverse proxy
At the moment, Jenkins is running on port 8080 but it is always recommended to use a reverse proxy.
So, install Nginx.
sudo apt install Nginx Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: fontconfig-config fonts-dejavu-core libdeflate0 libfontconfig1 libgd3 libgeoip1 libjbig0 libjpeg62-turbo libnginx-mod-http-geoip libnginx-mod-http-image-filter libnginx-mod-http-xslt-filter libnginx-mod-mail libnginx-mod-stream libnginx-mod-stream-geoip libtiff5 libwebp6 libx11-6 libx11-data libxau6 libxcb1 libxdmcp6 libxpm4 libxslt1.1 nginx-common nginx-core Suggested packages: libgd-tools geoip-bin fcgiwrap nginx-doc ssl-cert Recommended packages: geoip-database The following NEW packages will be installed: fontconfig-config fonts-dejavu-core libdeflate0 libfontconfig1 libgd3 libgeoip1 libjbig0 libjpeg62-turbo libnginx-mod-http-geoip libnginx-mod-http-image-filter libnginx-mod-http-xslt-filter libnginx-mod-mail libnginx-mod-stream libnginx-mod-stream-geoip libtiff5 libwebp6 libx11-6 libx11-data libxau6 libxcb1 libxdmcp6 libxpm4 libxslt1.1 nginx nginx-common nginx-core 0 upgraded, 26 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 5,678 kB of archives. After this operation, 13.9 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n]
Next, create a configuration file
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/jenkins.conf
And add the following
server {
server_name example.com www.example.com;
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
}
}
Replace the server_name value with your domain.
Save the changes and close the editor.
Also, you can secure access with Let’s Encrypt and Nginx.
Access to Jenkins
So, open your browser and access Jenkins through the domain. You will see the following screen.
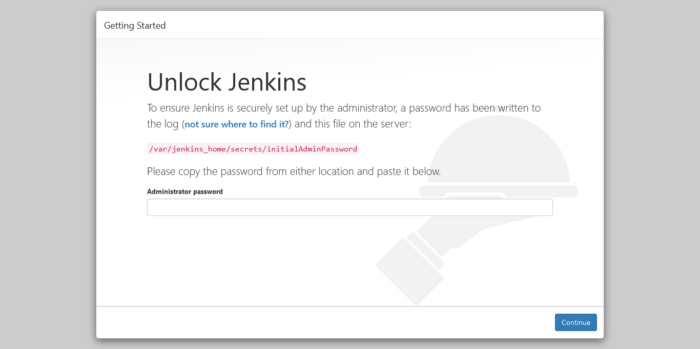
This indicates that the whole process has been successful and Jenkins has been successfully deployed.
Ah, to find out what is the password you have to run
docker exec -it jenkins cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword
In my case, this is the result.
59195b4d6c1642ceaeb5f3b259aa01d4
So, enjoy it.
Conclusion
In this post, you have learned how to run Jenkins using Docker and Docker Compose. We hope it has helped you and solved some doubts about these technologies.



