In this tutorial we will install ISPConfig on CentOS 8.
ISPConfig is an open source control panel for Linux. It has user friendly web interface. Using ISPConfig users can manage their websites, email addresses, FTP accounts, DNS records, databases and shell accounts.
Administrator, Reseller, Client, and Email-user are the four different levels of user access ISPConfig. Each of the user level have different kind of address.
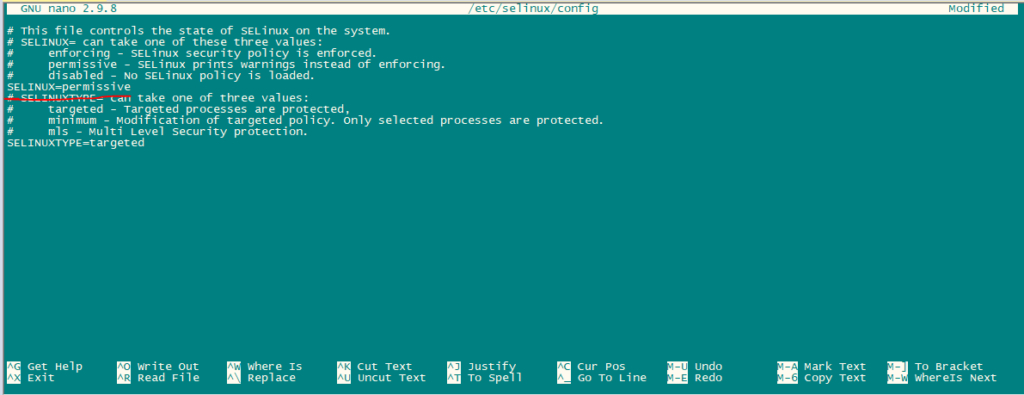
First, set SElinux to permissive mode.
nano /etc/selinux/configChange the mode from enable to permissive as shown in the below picture.
Now reboot the system.
rebootEnable Additional Repositories:
First, Import GPG key for software packages.
rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY*Enable Epel repository.
dnf -y install epel-release
Now we will activate power tools.
dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertoolsWe will now update using the following command:
dnf -y update
Install some additional packages.
dnf -y groupinstall 'Development Tools'
We have to Enable Remi Repository to get newer versions of PHP.
dnf install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm
dnf -y install yum-utils
dnf -y module reset php
dnf -y module install php:remi-7.4
dnf update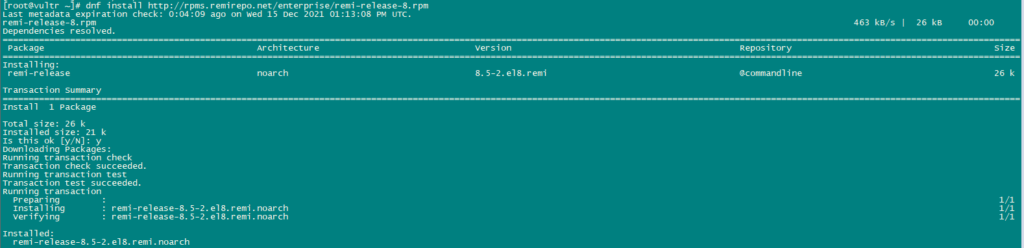
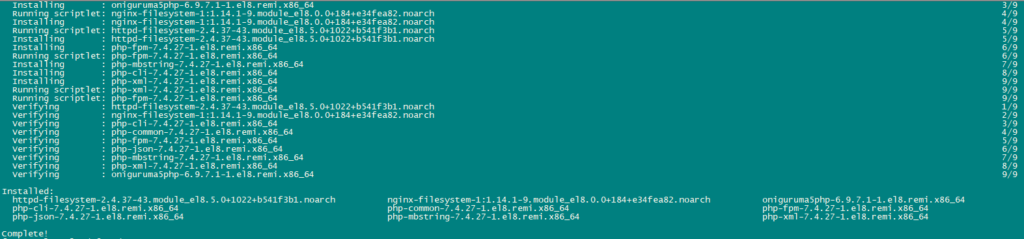
Use the following command to install required packages:
dnf -y install httpd mod_ssl mariadb-server php php-mysqlnd php-mbstring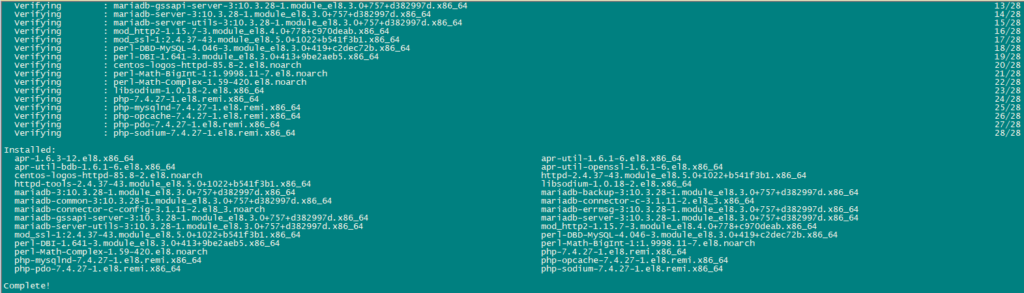
For security we will disable HTTP_PROXY header in apache globally using the following command:
echo "RequestHeader unset Proxy early" >> /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confRestart httpd service to apply configuration changes.
systemctl restart httpd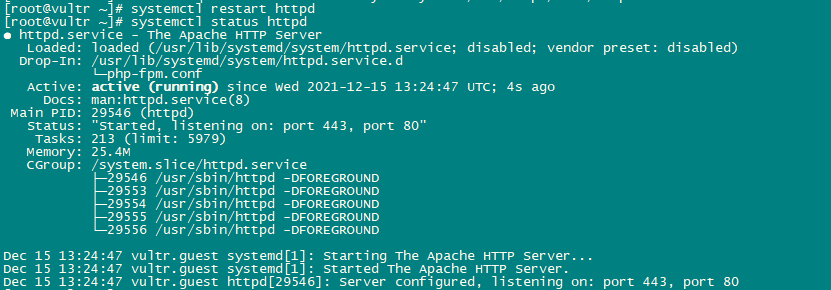
Now we will install PhpMyAdmin.
cd /tmp
wget https://files.phpmyadmin.net/phpMyAdmin/5.0.2/phpMyAdmin-5.0.2-all-languages.tar.gz
tar xzvf phpMyAdmin-5.0.2-all-languages.tar.gz
mkdir /usr/share/phpmyadmin
mv phpMyAdmin-5.0.2-all-languages/* /usr/share/phpmyadmin/
mkdir /usr/share/phpmyadmin/tmp
chown -R apache:apache /usr/share/phpmyadmin
chmod 777 /usr/share/phpmyadmin/tmp
Install Dovecot – Install ISPConfig on CentOS 8
We use the following commands to install dovecot.
dnf -y install dovecot dovecot-mysql dovecot-pigeonhole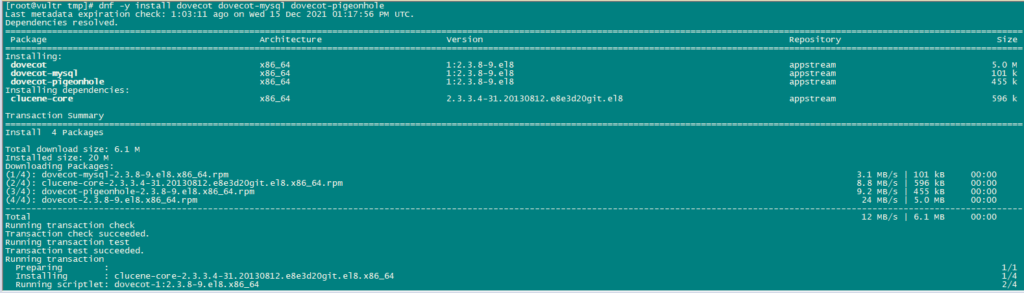
Create an empty configuration file and create symlinks with the main configuration file.
touch /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf
ln -s /etc/dovecot/dovecot-sql.conf /etc/dovecot-sql.conf
ln -s /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf /etc/dovecot.confNow Enable Dovecot so that it may automatically start to boot up. Also, start the service.
systemctl enable dovecot
systemctl start dovecot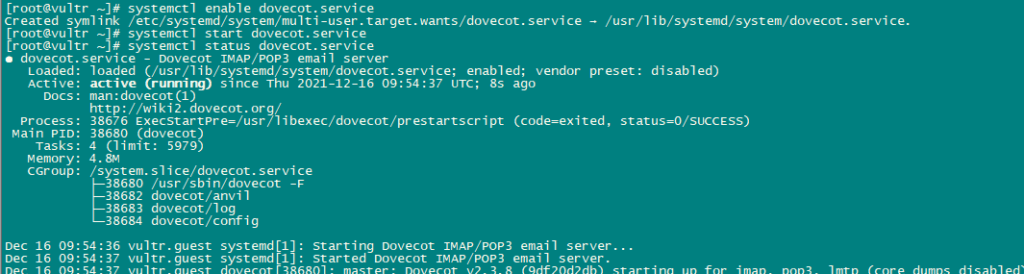
Install Postfix:
Use the following command to install postfix:
dnf -y install postfix postfix-mysql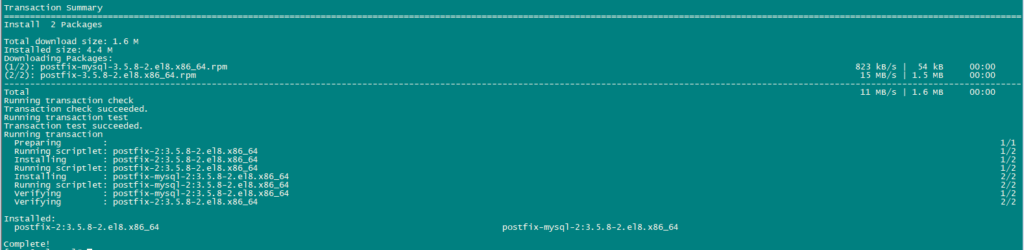
Now we will open the TLS/SSL and submission ports in postfix.
nano /etc/postfix/master.cfAfter editing the master.cf file it should look like this:
submission inet n - n - - smtpd
-o syslog_name=postfix/submission
-o smtpd_tls_security_level=encrypt
-o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes
-o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject
# -o smtpd_reject_unlisted_recipient=no
# -o smtpd_client_restrictions=$mua_client_restrictions
# -o smtpd_helo_restrictions=$mua_helo_restrictions
# -o smtpd_sender_restrictions=$mua_sender_restrictions
# -o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=
# -o smtpd_relay_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject
# -o milter_macro_daemon_name=ORIGINATING
smtps inet n - n - - smtpd
-o syslog_name=postfix/smtps
-o smtpd_tls_wrappermode=yes
-o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes
-o smtpd_client_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject
# -o smtpd_reject_unlisted_recipient=no
# -o smtpd_client_restrictions=$mua_client_restrictions
# -o smtpd_helo_restrictions=$mua_helo_restrictions
# -o smtpd_sender_restrictions=$mua_sender_restrictions
# -o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=
# -o smtpd_relay_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject
# -o milter_macro_daemon_name=ORIGINATINGJust changed the lines donot delete any content in the file just change the above mentioned lines.
Enable and Start Postfix and mariadb service.
systemctl enable mariadb.service
systemctl start mariadb.service
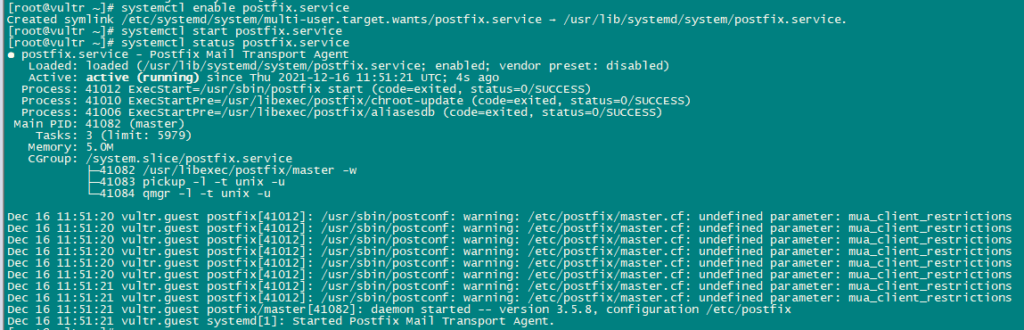
systemctl enable postfix.service
systemctl restart postfix.service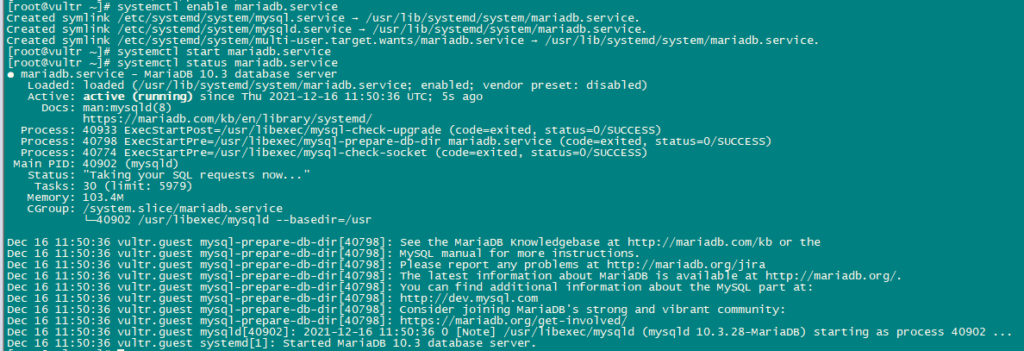
Install Getmail:
Use the following commands to install getmail:
dnf install python2
cd /tmp
wget http://pyropus.ca/software/getmail/old-versions/getmail-5.14.tar.gz
tar xvfz getmail-5.14.tar.gz
cd getmail-5.14
python2 setup.py build
python2 setup.py install
Now we will set MYSQL Password and configure phpMyAdmin.
Use the following command for mariadb configuration:
mysql_secure_installationSet all the configurations as below:
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Now we will Configure phpmyadmin.
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpmyadmin.confAdd the following lines in the file:
# phpMyAdmin - Web based MySQL browser written in php
#
# Allows only localhost by default
#
# But allowing phpMyAdmin to anyone other than localhost should be considered
# dangerous unless properly secured by SSL
Alias /phpMyAdmin /usr/share/phpmyadmin
Alias /phpmyadmin /usr/share/phpmyadmin
<Directory /usr/share/phpmyadmin/>
<IfModule mod_authz_core.c>
# Apache 2.4
# <RequireAny>
# Require ip 127.0.0.1
# Require ip ::1
# </RequireAny>
</IfModule>
<IfModule !mod_authz_core.c>
# Apache 2.2
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from All
Allow from 127.0.0.1
Allow from ::1
</IfModule>
</Directory>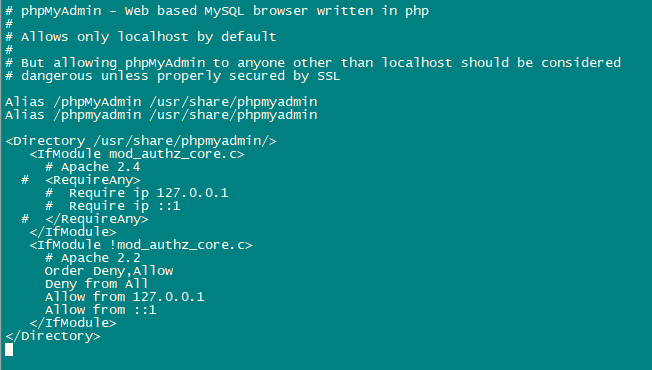
Next, we will change the authentication in phpMyAdmin from cookie to http.
cp -pf /usr/share/phpmyadmin/config.sample.inc.php /usr/share/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php
nano /usr/share/phpmyadmin/config.inc.phpChange the following line:
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['auth_type'] = 'http';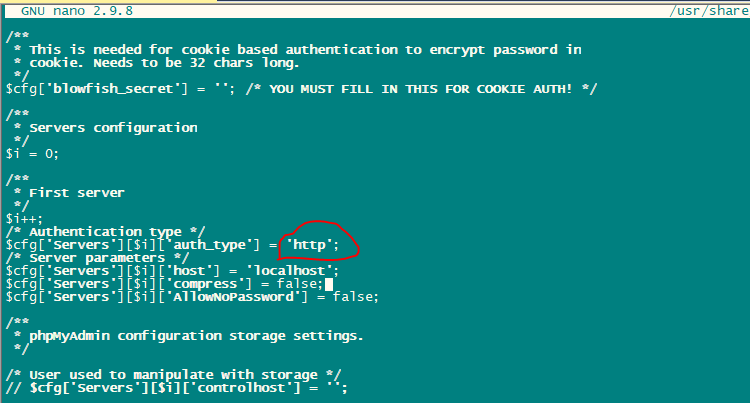
Enable and Start Apache Service.
systemctl enable httpd
systemctl restart httpd
Install Amavisd-new, SpamAssassin, ClamAV, and Postgrey:
We will install amavisd-new, SpamAssassin and ClamAV using the following command:
dnf -y install amavisd-new spamassassin clamav-server clamav-data clamav-update clamav-filesystem clamav clamav-scanner-systemd clamav-devel clamav-lib clamav-server-systemd unzip bzip2 perl-DBD-mysql postgrey re2c
Next, we will enable and start these services.
sa-update
freshclam
systemctl enable amavisd.service
systemctl start amavisd.service
systemctl start [email protected]
systemctl enable postgrey.service
systemctl start postgrey.service
Now we will configure postgrey service.
nano /etc/sysconfig/postgrey
Change the following line
POSTGREY_TYPE="--unix=/var/spool/postfix/postgrey/socket"
to
POSTGREY_TYPE="--inet=10023"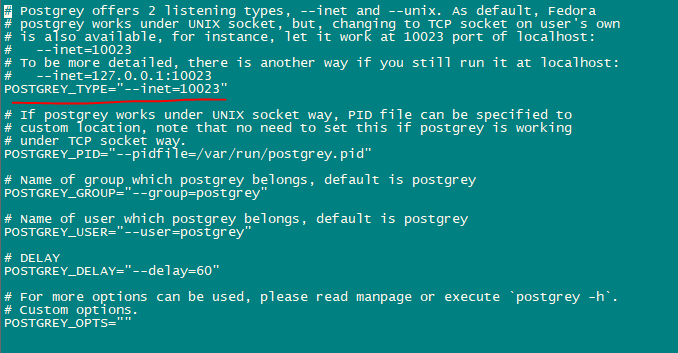
save and quit the file and restart postgrey service.
systemctl restart postgrey.serviceNow Configure Amivisd.
nano /etc/clamd.d/amavisd.conf
change the following line
LocalSocket /run/clamd.amavisd/clamd.sock
to
LocalSocket /var/spool/amavisd/clamd.sock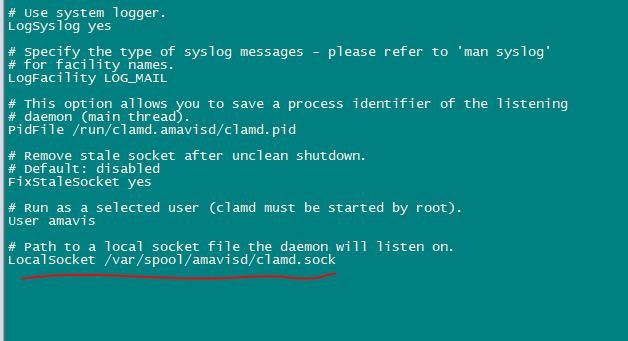
save and quit the file and restart clamAV service.
systemctl restart [email protected]
systemctl status [email protected]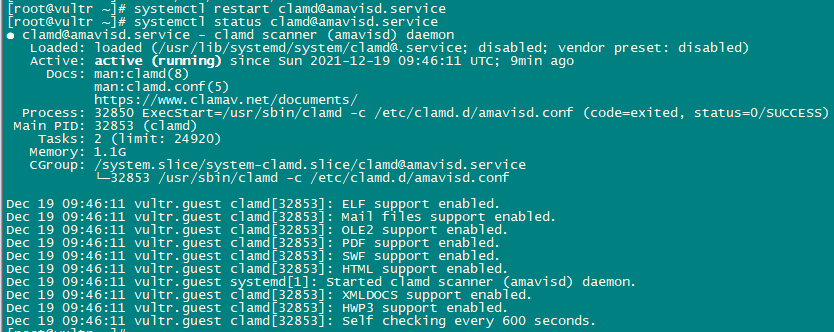
Now we will create freshclam as a service so that it can be started and stopped using systemctl. For this to work we will have to create a file having the path /usr/lib/systemd/system/freshclam.service.
nano /usr/lib/systemd/system/freshclam.serviceAdd the following content to the file:
[Unit]
Description = ClamAV Scanner
After = network.target
[Service]
Type = forking
# if you want to scan more than one in a day change the number 1 with your desired number in below line.
ExecStart = /usr/bin/freshclam -d -c 1
Restart = on-failure
PrivateTmp =true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target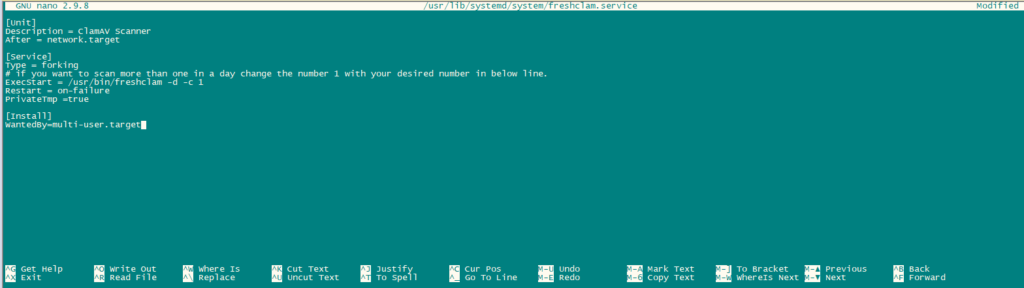
save and exit the file.
Now Enable and start the service.
systemctl enable freshclam.service
systemctl start freshclam.service
systemctl status freshclam.service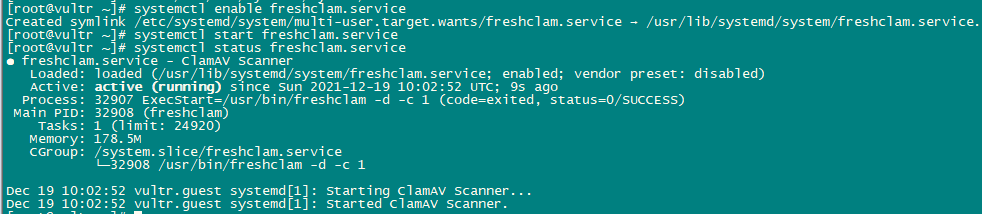
Install Apache with mod_php, mod_fcgi/PHP, PHP-FPM:
ISPConfig 3 allows you to use mod_php, mod_fcgi/PHP, cgi/PHP, and PHP-FPM as per website basis.
Install Apache2 with mod_php, mod_fcgid, and PHP using the following command:
dnf -y install php php-devel php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-mysql php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-pecl-apc php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-snmp php-soap php-tidy curl curl-devel perl-libwww-perl ImageMagick libxml2 libxml2-devel mod_fcgid php-cli httpd-devel php-fpm php-intl php-imagick php-pspell wgetNow we will configure php.ini file.
nano /etc/php.iniChange the error reporting so that notice won’t be shown, set the timezone and uncomment the line “cgi.fix_pathinfo=1“.
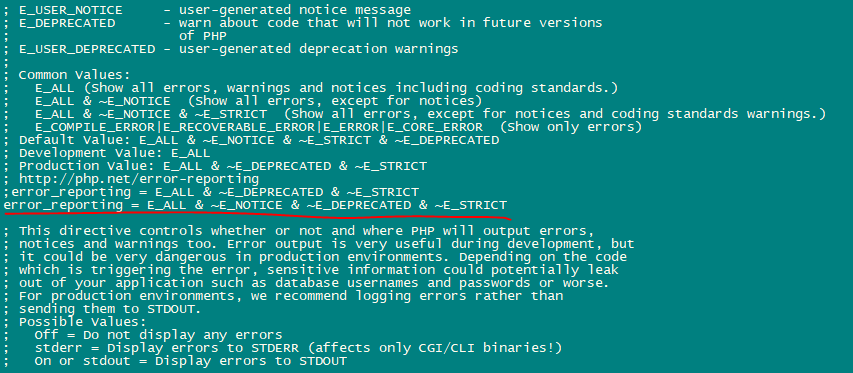
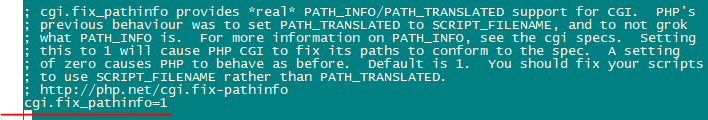
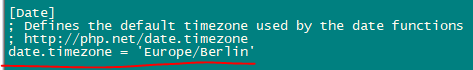
Enable httpd and PHP-FPM so that service can start at boot time and start the PHP-FPM service.
systemctl start php-fpm.service
systemctl enable php-fpm.service
systemctl status php-fpm.service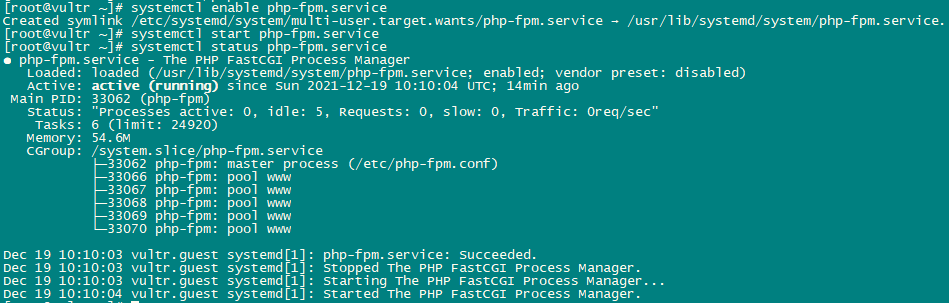
Now enable and restart apache service.
systemctl enable httpd.service
systemctl restart httpd.service
systemctl status httpd.service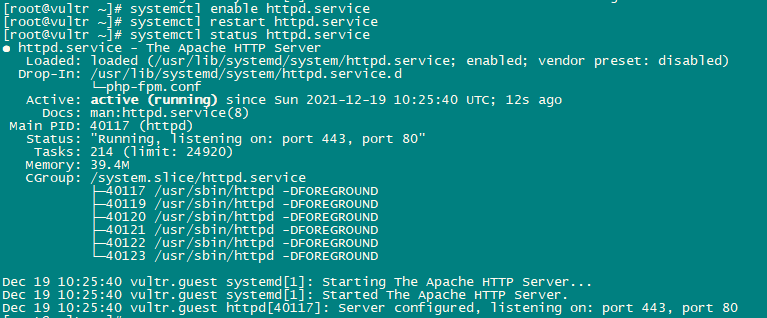
Now we will add support for Let’s encrypt. ISPConfig uses acme.sh as Let’s Encrypt client. Install acme.sh using the following command:
curl https://get.acme.sh | sh -s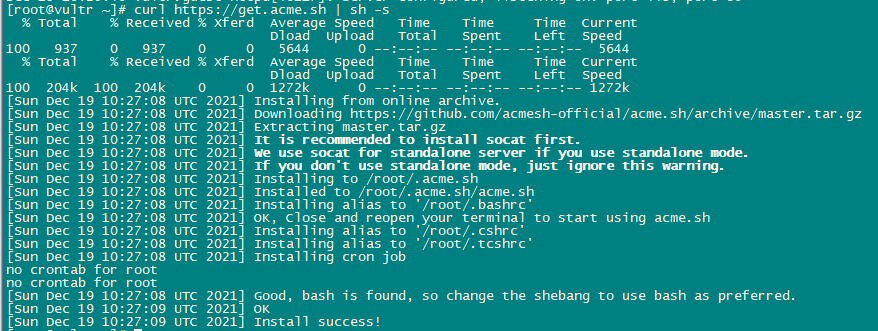
Installation of mod_python:
mod_python is a module of apache. It is not available as RPM so we will have to compile it from source. First, we will install python development files and then download current version of mod_python tar.gz file.
dnf -y install python3-devel
cd /usr/local/src/
wget http://dist.modpython.org/dist/mod_python-3.5.0.tgz
tar xfz mod_python-3.5.0.tgz
cd mod_python-3.5.0
Now we will configure and compile mod_python.
./configure --with-python=/usr/bin/python3
makeThere is an error in the compiled module which will cause the installation to fail with the error “version = “fatal: Not a git repository (or any of the parent directories): .git“. To resolve that error, run this sed command (the command is one line!).
sed -e 's/(git describe --always)/(git describe --always 2>\/dev\/null)/g' -e 's/`git describe --always`/`git describe --always 2>\/dev\/null`/g' -i $( find . -type f -name Makefile\* -o -name version.sh )Now install the module using the following command:
make install
Enable the module in Apache using the following command:
echo 'LoadModule python_module modules/mod_python.so' > /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/10-python.conf
systemctl restart httpd.service
systemctl status httpd.service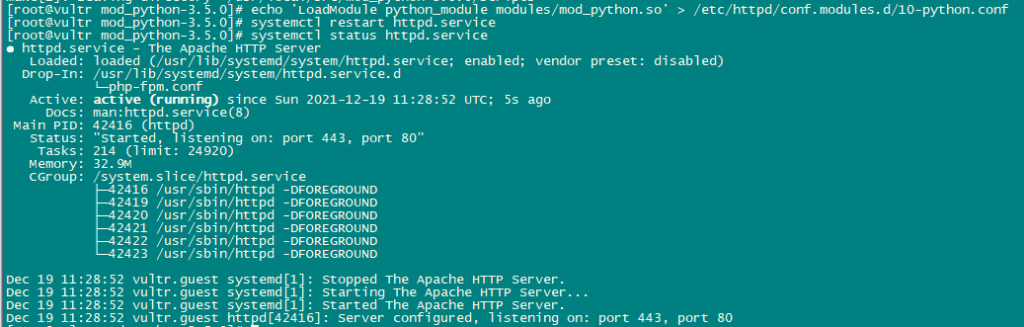
Install PureFTPd:
PureFTPd can be installed using the following command:
dnf -y install pure-ftpd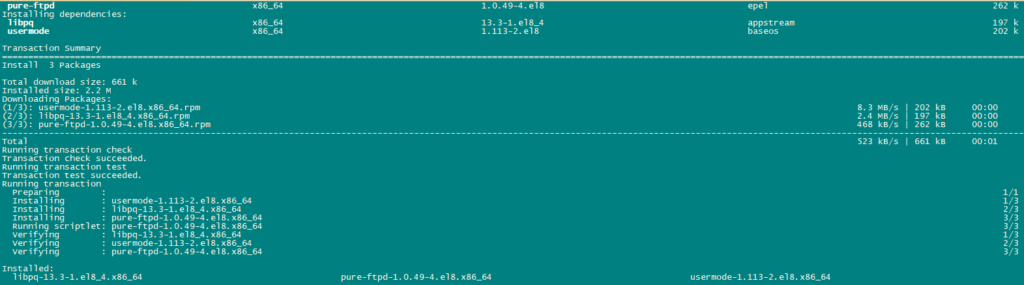
Enable and Start PureFTPd service.
systemctl enable pure-ftpd.service
systemctl start pure-ftpd.service
systemctl status pure-ftpd.service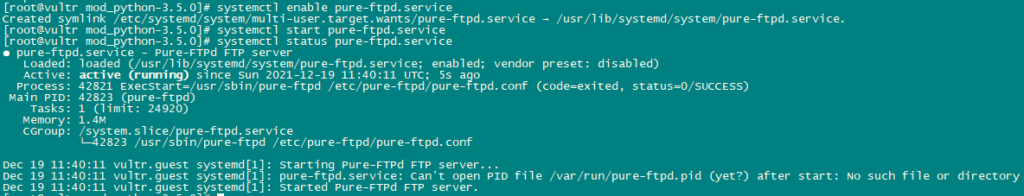
Now, we will configure PureFTPd to allow FTP and TLS sessions. FTP is a very insecure protocol because all passwords and data are transferred in clear text. By using TLS, the whole communication can be encrypted, thus making FTP much more secure.
OpenSSL is needed by TLS; to install OpenSSL use the following command:
dnf install opensslOpen /etc/pure-ftpd/pure-ftpd.conf and Enable TLS.
nano /etc/pure-ftpd/pure-ftpd.confAllow FTP and TLS sessions, set TLS to 1 by removing the # in front of the TLS line. It is highly recommended to enable TLS.
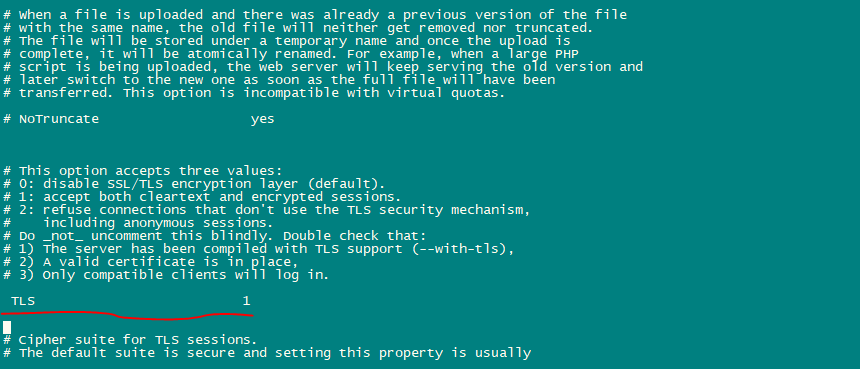
In order to use TLS, we must create an SSL certificate. create it in /etc/ssl/private/, therefore we will ceate that directory first:
mkdir -p /etc/ssl/private/Now, we will generate an SSL certificate using the following command:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 7300 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem -out /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem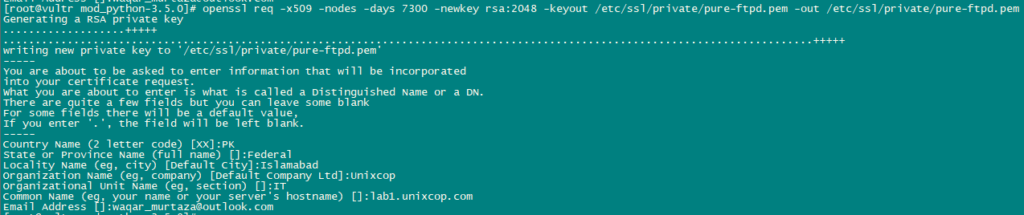
Change the permissions of the SSL certificate:
chmod 600 /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pemNow, Create a DHParam file using the following command:
openssl dhparam -out /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd-dhparams.pem 2048
Restart PureFTPd Service to apply all configurations.
systemctl restart pure-ftpd.service
systemctl status pure-ftpd.service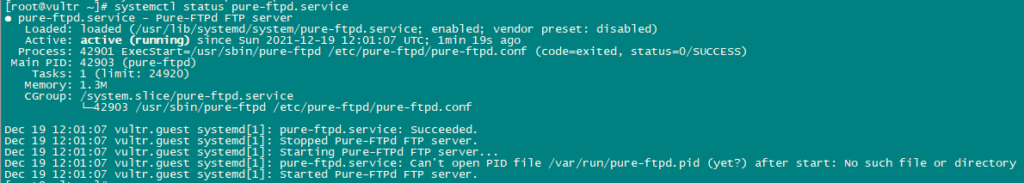
Install BIND:
Install BIND using the following command:
dnf -y install bind bind-utils haveged
We will configure BIND as per our need therefore, Take backup of existing configuration file and create a new one as follows:
cp /etc/named.conf /etc/named.conf_bak
cat /dev/null > /etc/named.conf
nano /etc/named.confAdd the following lines in the configuration file.
//
// named.conf
//
// Provided by Red Hat bind package to configure the ISC BIND named(8) DNS
// server as a caching only nameserver (as a localhost DNS resolver only).
//
// See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files.
//
options {
listen-on port 53 { any; };
listen-on-v6 port 53 { any; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
allow-query { any; };
allow-recursion {"none";};
recursion no;
};
logging {
channel default_debug {
file "data/named.run";
severity dynamic;
};
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.conf.local";save and exit the file.
Create the file /etc/named.conf.local that is included at the end of /etc/named.conf “/etc/named.conf.local” will later on get populated by ISPConfig if you create DNS zones in ISPConfig.
touch /etc/named.conf.localEnable and Start BIND and havege.
systemctl enable named.service
systemctl start named.service
systemctl status named.service
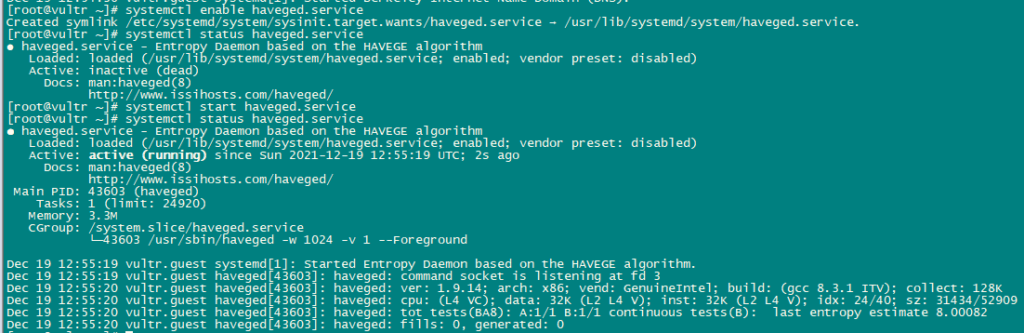
systemctl enable haveged.service
systemctl start haveged.service
systemctl status haveged.service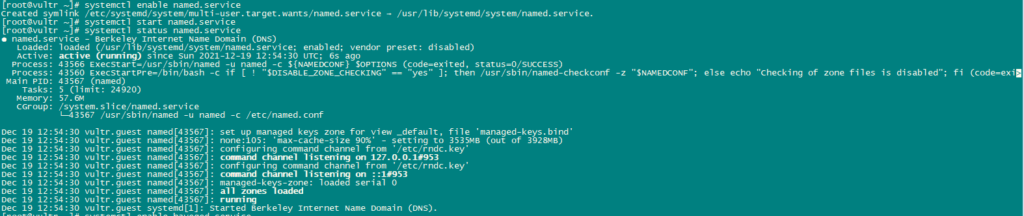
Install AWStats:
AWStats is a web statistics application. Use the following command to install AWStats:
dnf -y install awstats perl-DateTime-Format-HTTP perl-DateTime-Format-Builder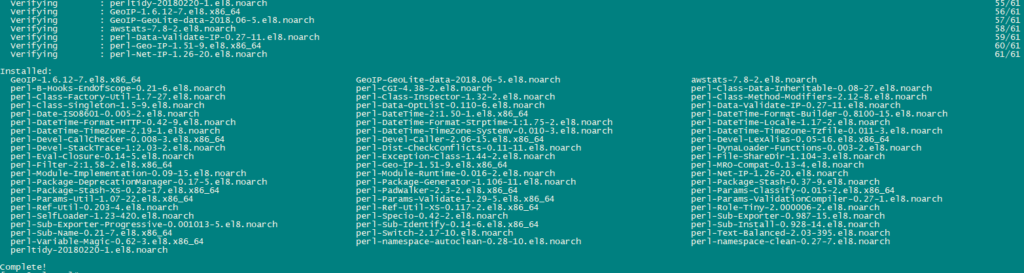
Install Jailkit:
We will use Jailkit to chroot SSH users and cronjobs. It can be installed as follows:
ln -s /usr/bin/python2 /usr/bin/python
cd /tmp
wget http://olivier.sessink.nl/jailkit/jailkit-2.21.tar.gz
tar xvfz jailkit-2.21.tar.gz
cd jailkit-2.21
./configure
make
make install
cd ..
rm -rf jailkit-2.21*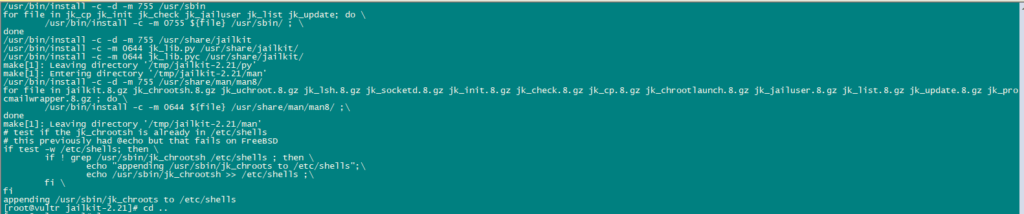
Install Fail2Ban:
Fail2Ban is optional but recommended, because the ISPConfig monitor tries to show the log.
Use the following command to install Fail2Ban.
dnf -y install iptables-services fail2ban fail2ban-systemd
systemctl stop firewalld.service
systemctl mask firewalld.service
systemctl disable firewalld.service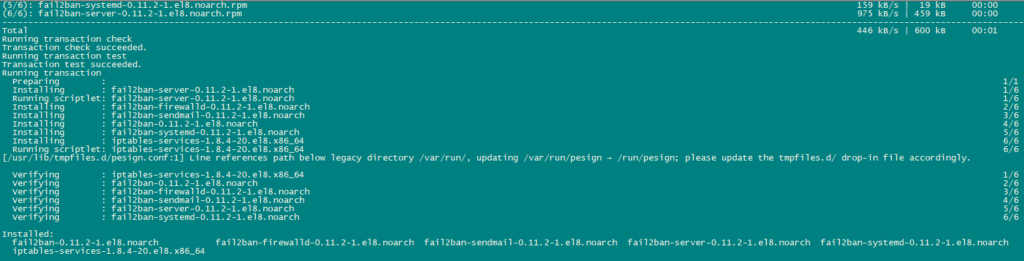
Next, create the /etc/fail2ban/jail.local file and enable monitoring for ssh, email and ftp service.
nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.localAdd the following lines in the file:
[sshd]
enabled = true
action = iptables[name=sshd, port=ssh, protocol=tcp]
[pure-ftpd]
enabled = true
action = iptables[name=FTP, port=ftp, protocol=tcp]
maxretry = 3
[dovecot]
enabled = true
action = iptables-multiport[name=dovecot, port="pop3,pop3s,imap,imaps", protocol=tcp]
maxretry = 5
[postfix-sasl]
enabled = true
action = iptables-multiport[name=postfix-sasl, port="smtp,smtps,submission", protocol=tcp]
maxretry = 3Enable and Start Fail2Ban Service.
systemctl enable fail2ban.service
systemctl start fail2ban.service
systemctl status fail2ban.service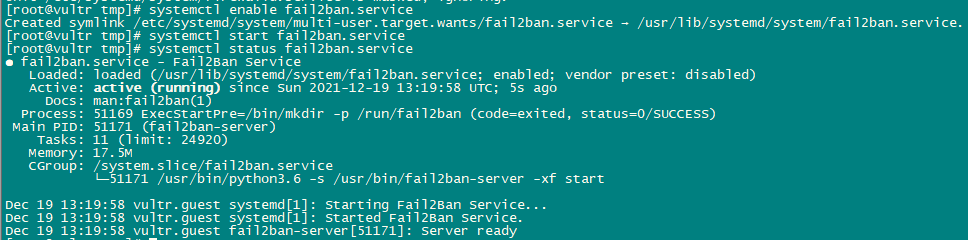
Install rkhunter:
We will now Install rkhunter using the following command:
dnf -y install rkhunter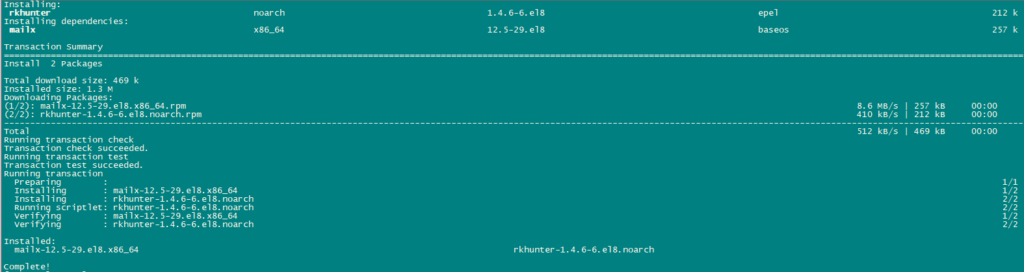
Install Mailman:
If you like to manage mailing lists with Mailman on your server, then install mailman now. Mailman is supported by ISPConfig, so you will be able to create new mailing lists through ISPConfig later.
dnf -y install mailman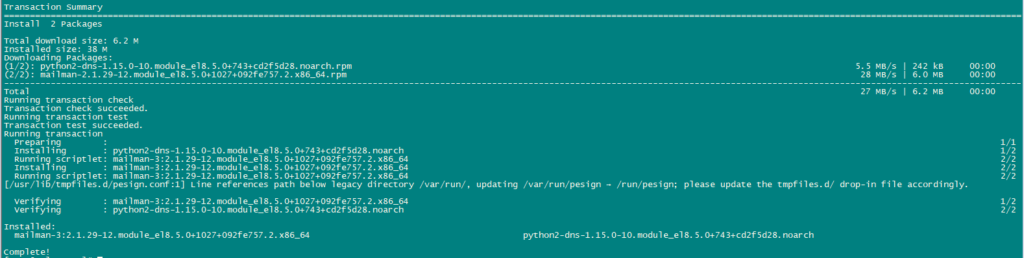
Before starting mailman, create a mailing list called mailman.
touch /var/lib/mailman/data/aliases
postmap /var/lib/mailman/data/aliases
/usr/lib/mailman/bin/newlist mailman
ln -s /usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman /usr/bin/mailman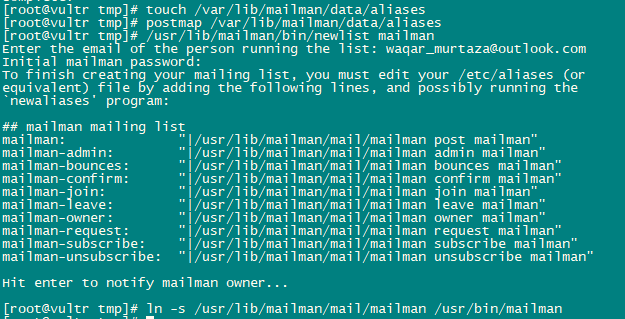
Open Aliases using the following command:
nano /etc/aliasesAdd the following lines in the file:
mailman: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman post mailman"
mailman-admin: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman admin mailman"
mailman-bounces: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman bounces mailman"
mailman-confirm: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman confirm mailman"
mailman-join: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman join mailman"
mailman-leave: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman leave mailman"
mailman-owner: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman owner mailman"
mailman-request: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman request mailman"
mailman-subscribe: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman subscribe mailman"
mailman-unsubscribe: "|/usr/lib/mailman/mail/mailman unsubscribe mailman"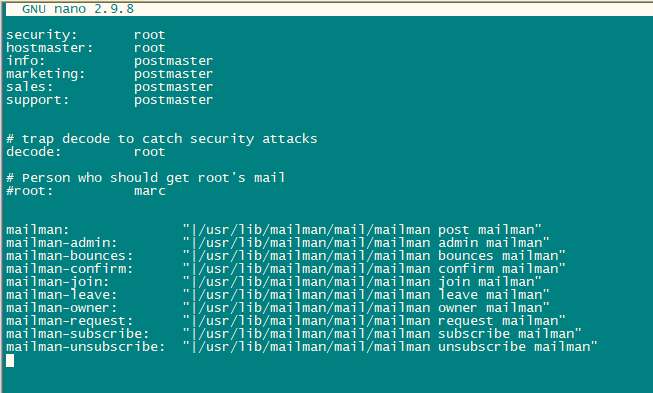
Run the following command to apply newly added configuration:
newaliasesRestart Postfix.
systemctl restart postfix.serviceWe will configure Apache mailman configuration file.
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/mailman.confAdd the line ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/mailman/ /usr/lib/mailman/cgi-bin/. Comment out Alias /pipermail/ /var/lib/mailman/archives/public/ and add the line Alias /pipermail /var/lib/mailman/archives/public/.
After editing file will look like this:
#
# httpd configuration settings for use with mailman.
#
ScriptAlias /mailman/ /usr/lib/mailman/cgi-bin/
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/mailman/ /usr/lib/mailman/cgi-bin/
<Directory /usr/lib/mailman/cgi-bin/>
AllowOverride None
Options ExecCGI
Require all granted
</Directory>
#Alias /pipermail/ /var/lib/mailman/archives/public/
Alias /pipermail /var/lib/mailman/archives/public/
<Directory /var/lib/mailman/archives/public>
Options MultiViews FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
AddDefaultCharset Off
</Directory>
# Uncomment the following line, replacing www.example.com with your server's
# name, to redirect queries to /mailman to the listinfo page (recommended).
# RedirectMatch ^/mailman[/]*$ http://www.example.com/mailman/listinfo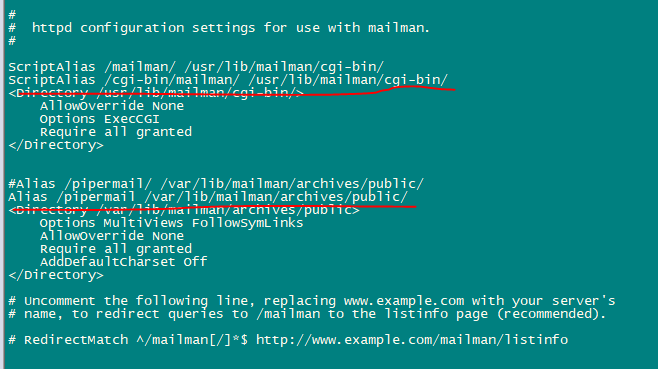
Restart Apache Service to apply configurations.
systemctl restart httpd.serviceEnable and Start Mailman Service.
systemctl enable mailman.service
systemctl start mailman.service
systemctl status mailman.service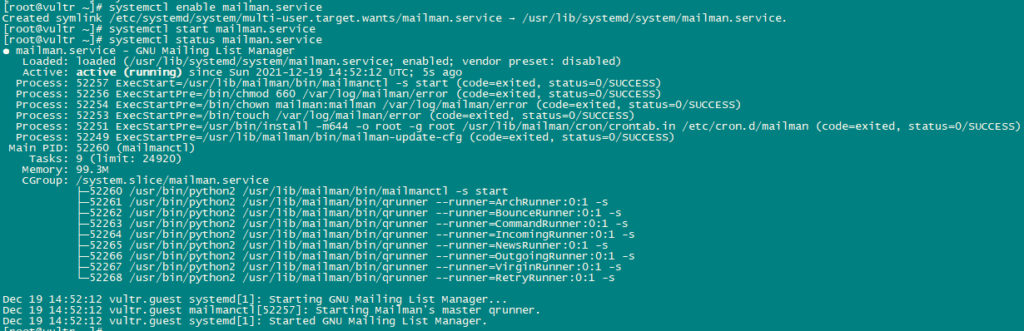
After You will Install ISPConfig 3 you can use Mailman as follows:
You can use the alias /cgi-bin/mailman for all Apache vhosts (please note that suExec and CGI must be disabled for all vhosts from which you want to access Mailman!), which means you can access the Mailman admin interface for a list at http:///cgi-bin/mailman/admin/, and the web page for users of a mailing list can be found at http:///cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/.
Under http:///pipermail/ you can find the mailing list archives.
Install Roundcube webmail:
We will download Roundcube webmail using wget and then install it.
cd /tmp
wget https://github.com/roundcube/roundcubemail/releases/download/1.4.3/roundcubemail-1.4.3-complete.tar.gz
Unpack the tar.gz file and move the RoundCube source to /usr/share/roundcubemail.
tar xfz roundcubemail-1.4.3-complete.tar.gz
mkdir /usr/share/roundcubemail
mv /tmp/roundcubemail-1.4.3/* /usr/share/roundcubemail/
chown -R root:root /usr/share/roundcubemail
chown apache /usr/share/roundcubemail/temp
chown apache /usr/share/roundcubemail/logscreate a roundcube configuration file.
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/roundcubemail.confAdd the following lines in the file:
#
# Round Cube Webmail is a browser-based multilingual IMAP client
#
Alias /roundcubemail /usr/share/roundcubemail
Alias /webmail /usr/share/roundcubemail
# Define who can access the Webmail
# You can enlarge permissions once configured
<Directory /usr/share/roundcubemail/>
Options none
AllowOverride Limit
Require all granted
</Directory>
# Define who can access the installer
# keep this secured once configured
<Directory /usr/share/roundcubemail/installer>
Options none
AllowOverride Limit
Require all granted
</Directory>
# Those directories should not be viewed by Web clients.
<Directory /usr/share/roundcubemail/bin/>
Order Allow,Deny
Deny from all
</Directory>
<Directory /usr/share/roundcubemail/plugins/enigma/home/>
Order Allow,Deny
Deny from all
</Directory>Restart Apache.
systemctl restart httpd.serviceNow we need a database for RoundCube mail, we will create it as follows:
mysql -u root -puse the following queries to create Database:
CREATE DATABASE roundcubedb;
CREATE USER roundcubeuser@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'roundcubepassword';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES on roundcubedb.* to roundcubeuser@localhost ;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
exit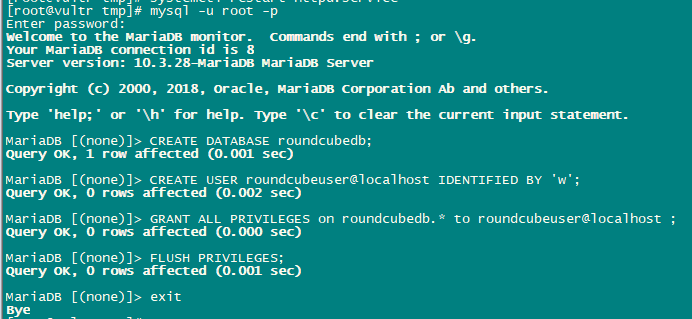
Now we will install RoundCube in the browser at http://YOUR_IPAddress/roundcubemail/installer/
Now create the config.inc.php file.
nano /usr/share/roundcubemail/config/config.inc.phpAdd the following lines in it:
<?php
/* Local configuration for Roundcube Webmail */
// ----------------------------------
// SQL DATABASE
// ----------------------------------
// Database connection string (DSN) for read+write operations
// Format (compatible with PEAR MDB2): db_provider://user:password@host/database
// Currently supported db_providers: mysql, pgsql, sqlite, mssql, sqlsrv, oracle
// For examples see http://pear.php.net/manual/en/package.database.mdb2.intro-dsn.php
// NOTE: for SQLite use absolute path (Linux): 'sqlite:////full/path/to/sqlite.db?mode=0646'
// or (Windows): 'sqlite:///C:/full/path/to/sqlite.db'
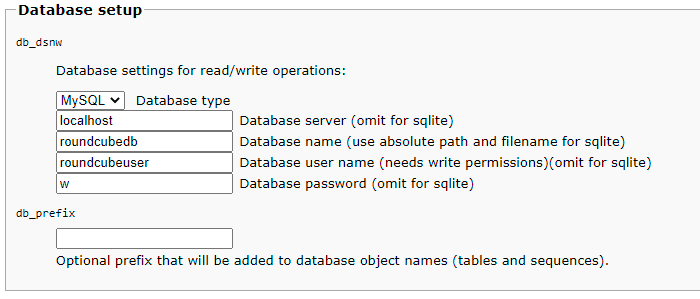
$config['db_dsnw'] = 'mysql://roundcubeuser:roundcubepassword@localhost/roundcubedb';
// ----------------------------------
// IMAP
// ----------------------------------
// The IMAP host chosen to perform the log-in.
// Leave blank to show a textbox at login, give a list of hosts
// to display a pulldown menu or set one host as string.
// To use SSL/TLS connection, enter hostname with prefix ssl:// or tls://
// Supported replacement variables:
// %n - hostname ($_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'])
// %t - hostname without the first part
// %d - domain (http hostname $_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] without the first part)
// %s - domain name after the '@' from e-mail address provided at login screen
// For example %n = mail.domain.tld, %t = domain.tld
// WARNING: After hostname change update of mail_host column in users table is
// required to match old user data records with the new host.
$config['default_host'] = 'localhost';
$config['smtp_server'] = 'localhost';
$config['smtp_port'] = 25;
// provide an URL where a user can get support for this Roundcube installation
// PLEASE DO NOT LINK TO THE ROUNDCUBE.NET WEBSITE HERE!
$config['support_url'] = '';
// This key is used for encrypting purposes, like storing of imap password
// in the session. For historical reasons it's called DES_key, but it's used
// with any configured cipher_method (see below).
$config['des_key'] = 'pb0UucO0eqjgvhrqYlFTBVjE';
// ----------------------------------
// PLUGINS
// ----------------------------------
// List of active plugins (in plugins/ directory)
$config['plugins'] = array();
// Set the spell checking engine. Possible values:
// - 'googie' - the default (also used for connecting to Nox Spell Server, see 'spellcheck_uri' setting)
// - 'pspell' - requires the PHP Pspell module and aspell installed
// - 'enchant' - requires the PHP Enchant module
// - 'atd' - install your own After the Deadline server or check with the people at http://www.afterthedeadline.com before using their API
// Since Google shut down their public spell checking service, the default settings
// connect to http://spell.roundcube.net which is a hosted service provided by Roundcube.
// You can connect to any other googie-compliant service by setting 'spellcheck_uri' accordingly.
$config['spellcheck_engine'] = 'pspell';
$config['enable_installer'] = true;Now click Next in the web browser:
Then press continue and you will enter a new page where It will give you the configurations. Just copy these configurations and paste on config.php.ini file.
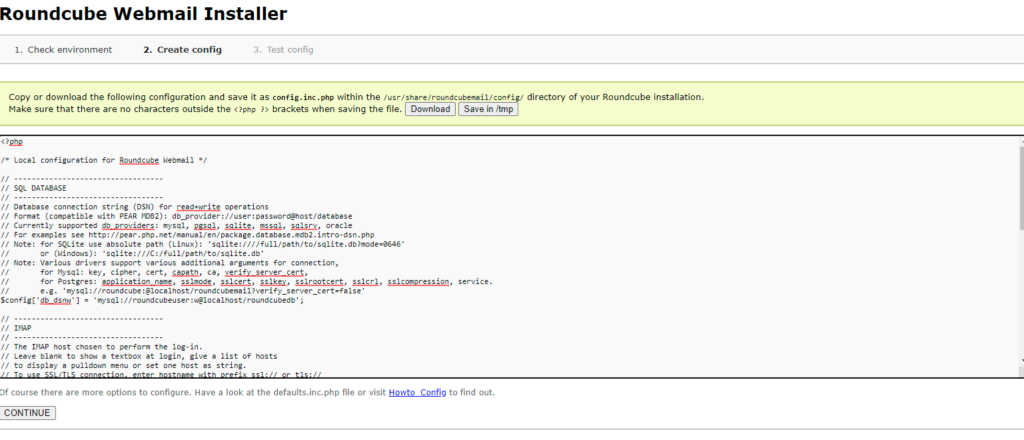
then initailize database.
Now, Open config file.
nano /usr/share/roundcubemail/config/config.inc.php
change the line:
$config['enable_installer'] = true;
to
$config['enable_installer'] = false;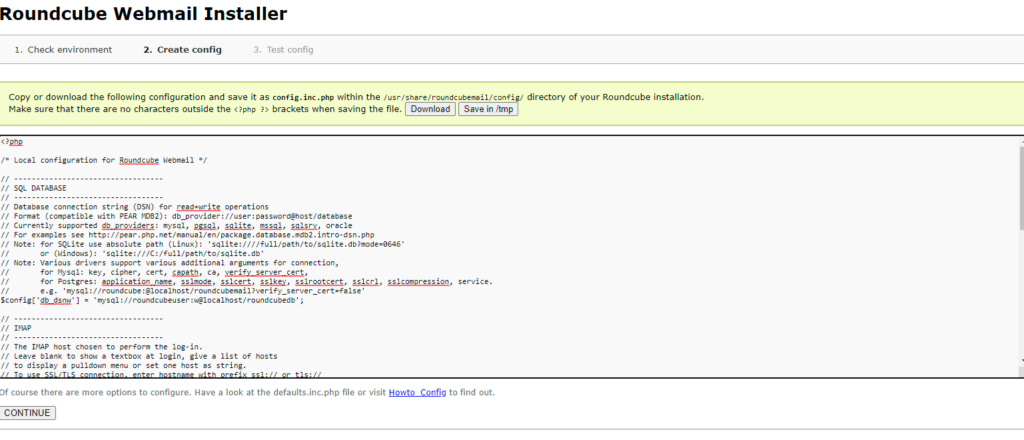
Roundcube is available now under the aliases /webmail and /roundcubemail on your server:
http://YOUR_IPAddress/webmail
The RoundCube login is the email address and password of an email account that you create later in ISPConfig.
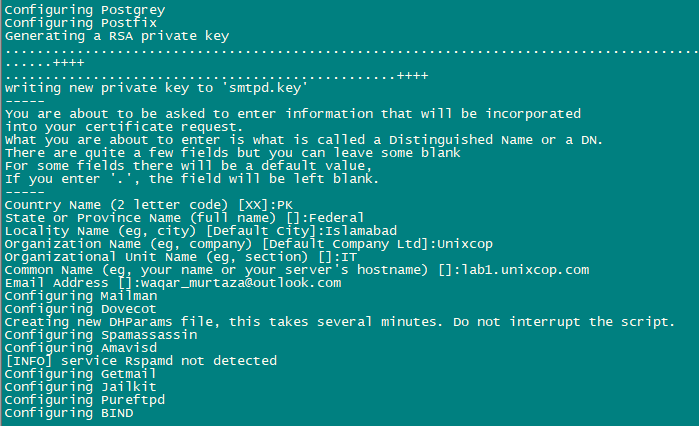
Install ISPConfig on CentOS 8
The ISPConfig installer will configure all services like Postfix, Dovecot, etc. for you.
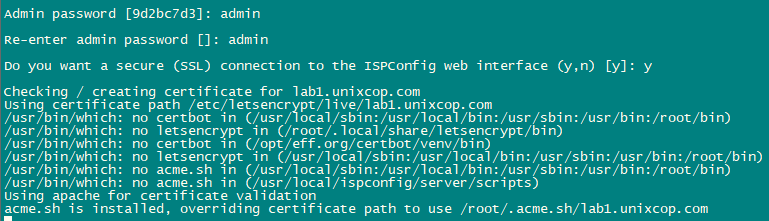
You also have the possibility to let the installer create an SSL vhost for the ISPConfig control panel
so that ISPConfig can be accessed using https:// instead of http://. To achieve this, just press ENTER when you see this question:
Do you want a secure (SSL) connection to the ISPConfig web interface (y,n) [y]:.
To install ISPConfig 3.2 nightly build, use the following commands:
cd /tmp
wget -O ispconfig.tar.gz https://www.ispconfig.org/downloads/ISPConfig-3-stable.tar.gz
tar xfz ispconfig.tar.gz
cd ispconfig3*/install/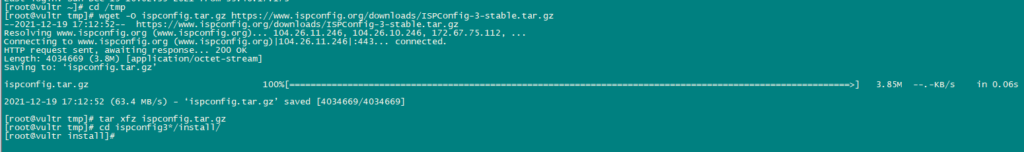
The next step is to run:
php -q install.php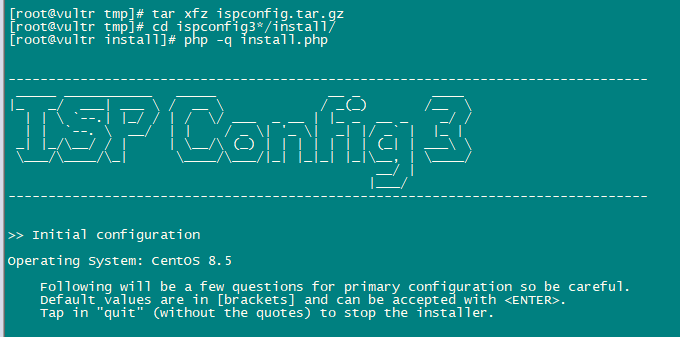
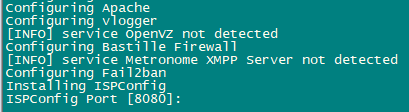
This will start the ISPConfig 3 installer. The installer will configure all services like Postfix, Dovecot, etc. for you.
Hit Enter if the value in bracket is what you want you set otherwise enter your desired value and press Enter.
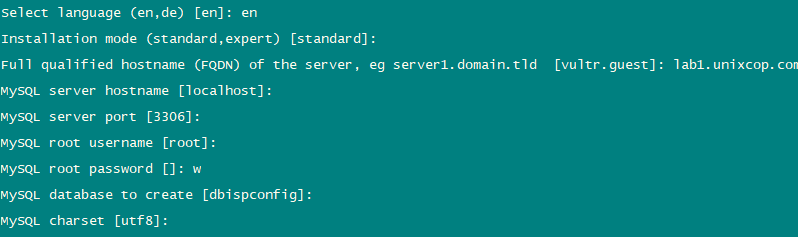
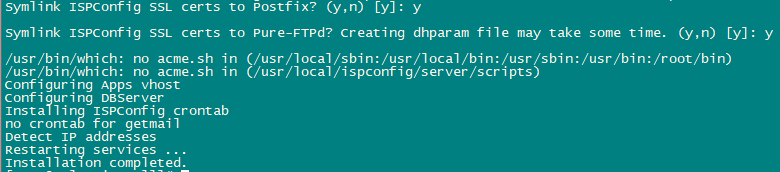
Installation is now complete.
Afterwards you can access ISPConfig 3 using https://YOUR-IPAddress:8080.
Login with admin as Username and Password. You should change the default password after first login.
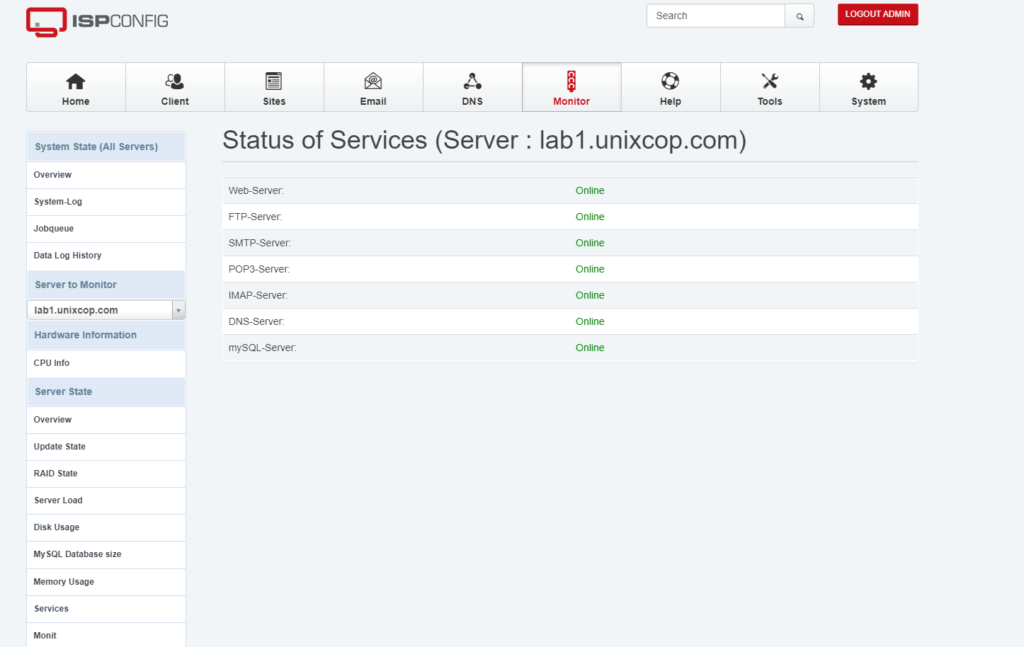
Now you can use ISPConfig as per your need.




Hello, i failed ” error 400 – trying to redirect ” after ispconfig. Help me fix this.