Want a more complete alternative to the du command? Well, in this post, we will show it to you because you will learn how to install and use the duf command on Linux.
Introduction
duf is a Disk Usage/Free Utility that is written in Go and is meant to be a solid alternative to the df command by presenting the information in a more user-friendly way.
Some of its main features are the following:
- User-friendly, colorful output
- Adjusts to your terminal’s theme & width
- Sort the results according to your needs
- Groups & filters devices
- Can conveniently output JSON
It is worth noting that the tool not only works on Linux systems, but can be used on BSD, macOS, Windows, and Android.
So, it is almost a must to know how to install it to get further information about disk usage.
Let’s go.
Install duf on Linux
We can install duf from many methods and even from the official repositories of Linux distributions.
In the case of Debian (unstable), Ubuntu, Linux Mint and other members of the family
sudo apt update
sudo apt install dufIf you are using Arch Linux, Manjaro or another derivative
sudo pacman -S dufBut don’t worry, there are packages DEB and RPM to support many other distributions.
Also on the tool’s GitHub site, you can find instructions on how to compile it and generate the binary yourself.
Using the duf command on Linux
Once you have already installed the duf command using any possible method for it, you can use it by executing in the terminal
dufYou will get an output screen like this
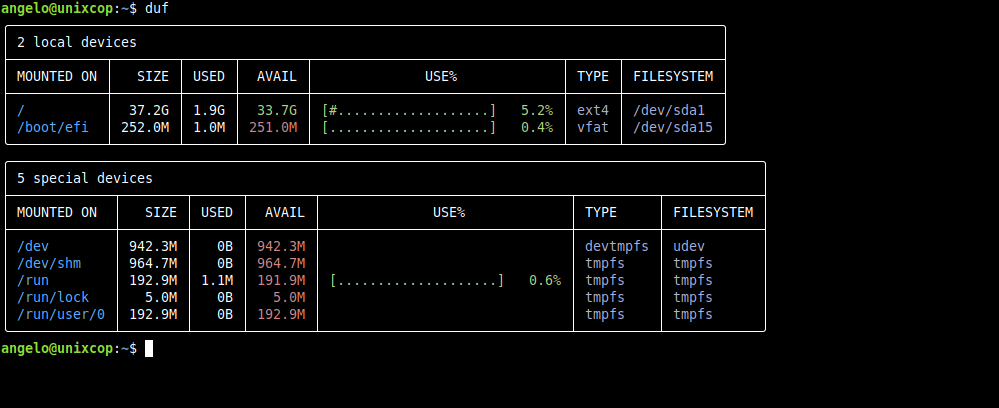
If you want to learn more ways to use it, you can show the help with the following command
duf --help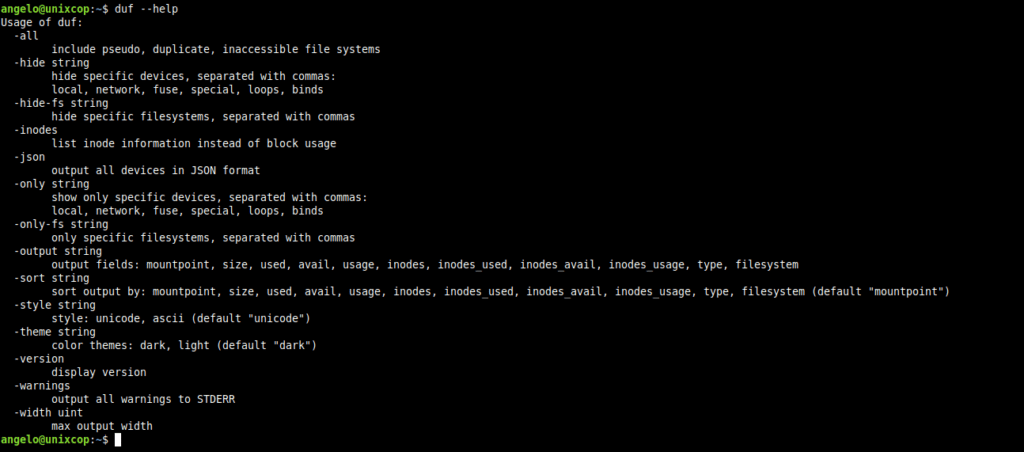
If you would like to list everything (including pseudo, duplicate, inaccessible file systems):
duf --all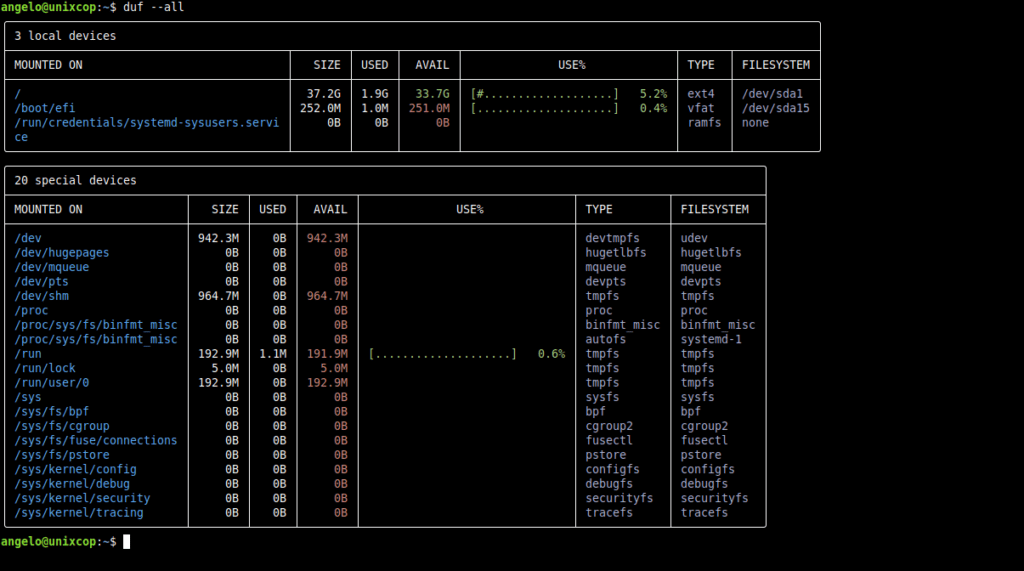
By adding arguments, you can display information about those locations
duf /home /varAs the information is massive, you can filter it by choosing what to show and what to hide.
duf --only local,network,fuse,special,loops,binds
duf --hide local,network,fuse,special,loops,bindsAnother way to improve the results, is to sort it by specific criteria. For example:
duf --sort size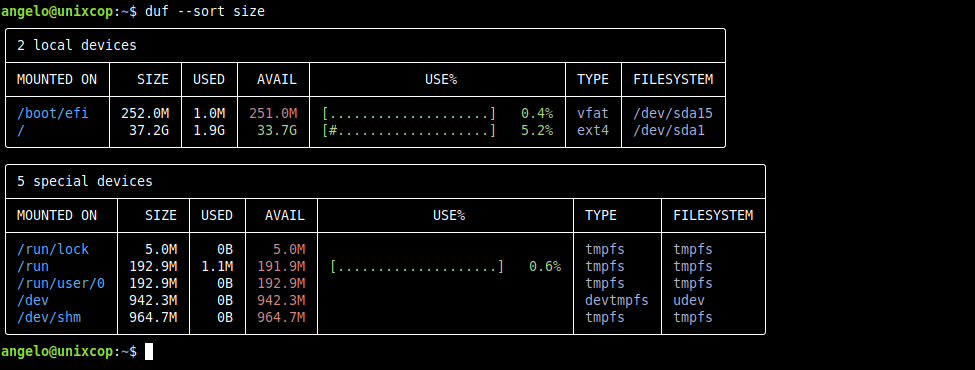
But you can use more criteria mountpoint, size, used, avail, usage, inodes, inodes_used, inodes_avail, inodes_usage, type, filesystem.
And to use the JSON features
duf --jsonSo, enjoy it.
Conclusion
In this post, you learned about the duf command on Linux. Therefore, you can know the disk space occupied on Linux and in a specific location.



