Introduction
In this article, we will learn how to install, update, remove, find packages, manage packages and repositories on Linux systems using YUM (Yellowdog Updater Modified) tool developed by RedHat. The example commands shown in this article are practically tested on our CentOS 8.3 server, you can use these material for study purpose, certifications or just to explore ways to install new packages and keep your system up-to-date. The basic requirement of this article is, you must have a basic understanding of commands and a working Linux operating system, where you can explore and practice all the commands listed below.
What is YUM?
YUM (Yellowdog Updater Modified) is an open source command-line as well as graphical based package management tool for RPM (RedHat Package Manager) based Linux systems. It allows users and system administrator to easily install, update, remove or search software packages on a systems. It was developed and released by Seth Vidal under GPL (General Public License) as an open source, means anyone can allowed to download and access the code to fix bugs and develop customized packages. YUM uses numerous third party repositories to install packages automatically by resolving their dependencies issues.
1. Install a Package with YUM
To install a package called Firefox , just run the below command it will automatically find and install all required dependencies for Firefox.
The above command will ask confirmation before installing any package on your system. If you want to install packages automatically without asking any confirmation, use option -y as shown in below example.
yum -y install firefox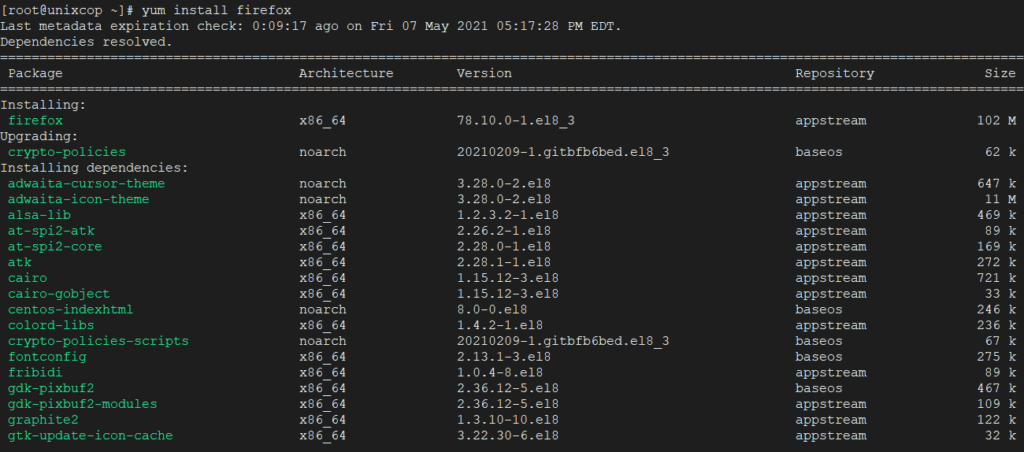
2. Removing a Package with YUM
To remove a package completely with their all dependencies, just run the following command as shown below.
Same way the above command will ask confirmation before removing a package. To disable confirmation prompt just add option -y as shown in below.
yum -y remove firefox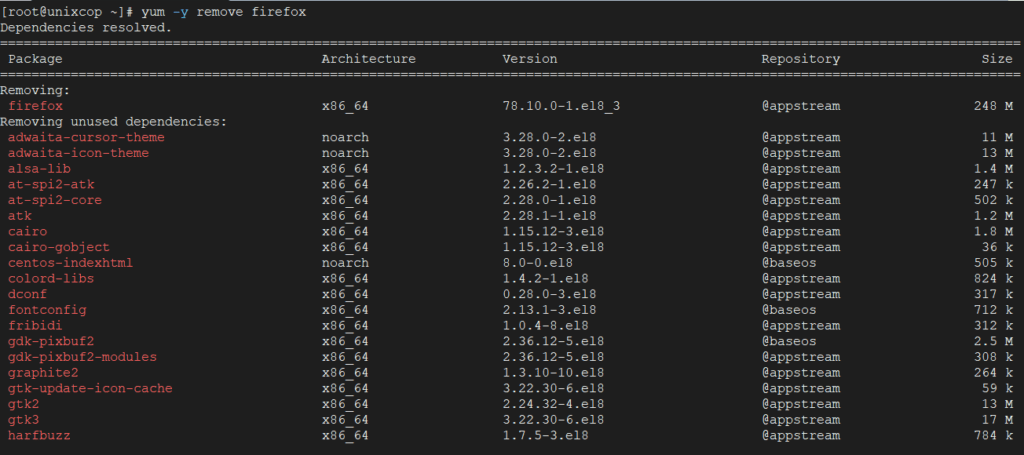
3. Updating a Package using YUM
Let’s say you have the VIM package and you want to update it to the latest stable version. Just run the following command it will automatically resolves all dependencies issues and install them.
yum update vim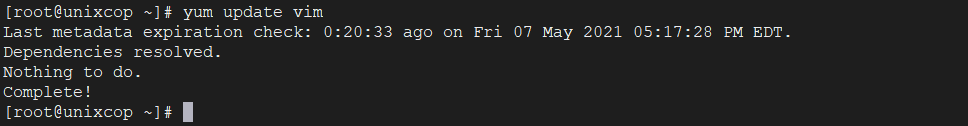
4. List a Package using YUM
Use the list function to search for the specific package with name. For example to search for a package called openssh, use the command.

To make your search more accurate, define package name with their version, in case you know. For example to search for a specific version openssh-4.3p2 of the package, use the command.
yum list openssh-4.3p25. Search for a Package using YUM
If you don’t remember the exact name of the package, then use search function to search all the available packages to match the name of the package you specified. For example, to search all the packages that matches the word .
yum search vsftpd
6. Get Information of a Package using YUM
Say you would like to know information of a package before installing it. To get information of a package just issue the below command.
yum info firefox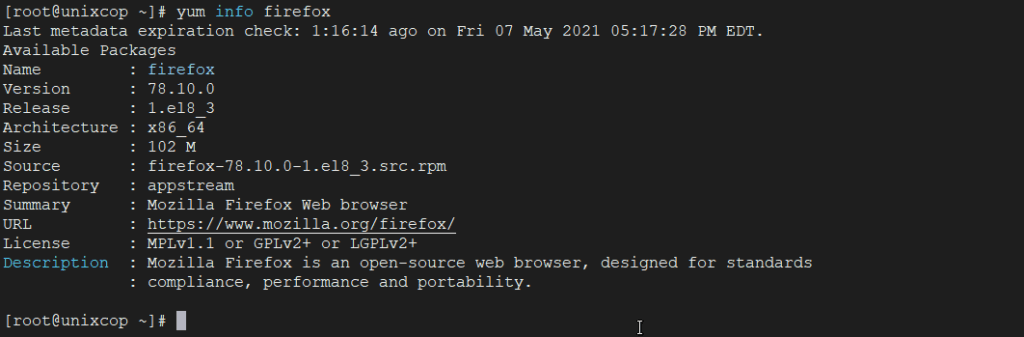
7. List all Available Packages using YUM
To list all the available packages in the Yum database, use the below command.
yum list | less
8. List all Installed Packages using YUM
To list all the installed packages on a system, just issue below command, it will display all the installed packages.
yum list installed | less
9. Yum Provides Function
Yum provides function is used to find which package a specific file belongs to. For example, if you would like to know the name of the package that has the /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf.
yum provides /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf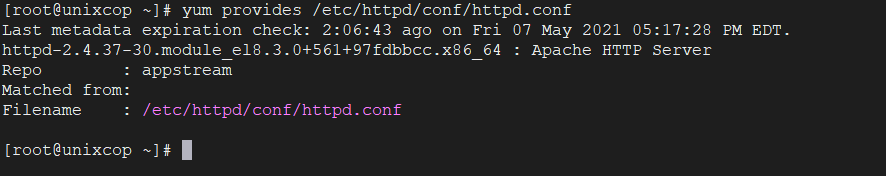
10. Check for Available Updates using Yum
To find how many of installed packages on your system have updates available, to check use the following command.
yum check-update
11. Update System using Yum
To keep your system up-to-date with all security and binary package updates, run the following command. It will install all latest patches and security updates to your system.
yum update12. List all available Group Packages
In Linux, number of packages are bundled to particular group. Instead of installing individual packages with yum, you can install particular group that will install all the related packages that belongs to the group. For example to list all the available groups, just issue following command.
yum grouplist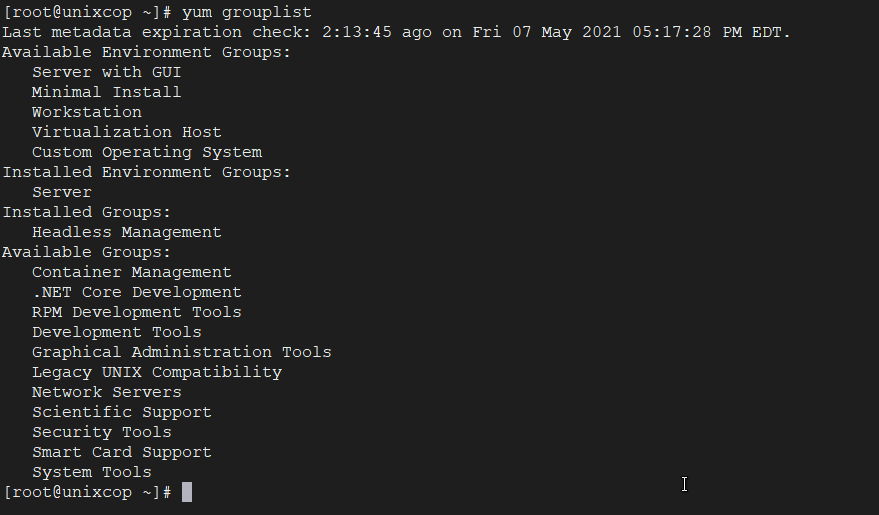
13. Install a Group Packages
To install a particular package group, we use option as groupinstall. Fore example, to install “Container Management“ group packages, just execute the below command.
yum groupinstall -y 'Container Management'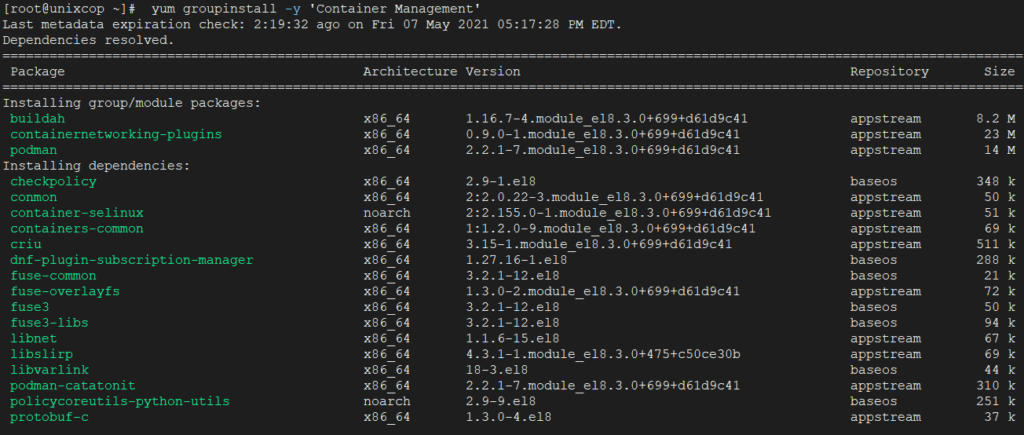
14. Update a Group Packages
To update any existing installed group packages, just run the following command as shown below.
yum groupupdate 'Container Management'15. Remove a Group Packages
To delete or remove any existing installed group from the system, just use below command.
yum groupremove 'Container Management'16. List Enabled Yum Repositories
To list all enabled Yum repositories in your system, use following option.
yum repolist
17. List all Enabled and Disabled Yum Repositories
The following command will display all enabled and disabled yum repositories on the system.
yum repolist all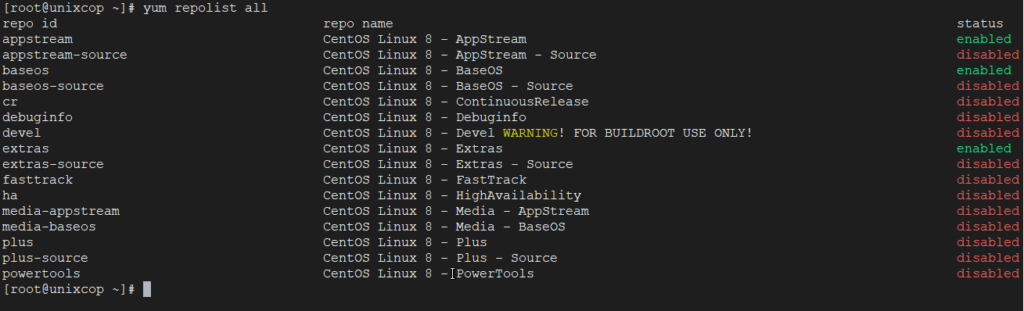
18. Install a Package from Specific Repository
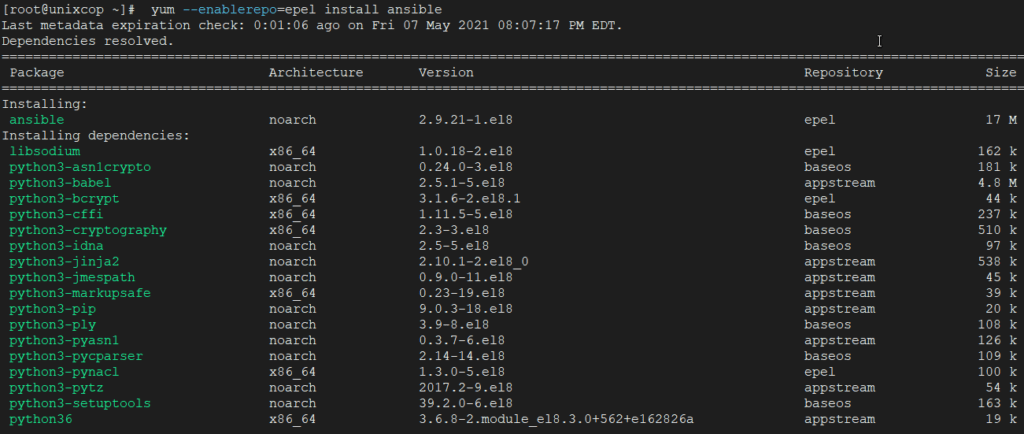
To install a particular package from a specific enabled or disabled repository, you must use –enablerepo option in your yum command. For example to Install Ansible package, just execute the command.
yum --enablerepo=epel install ansible
19. Interactive Yum Shell
Yum utility provides a custom shell where you can execute multiple commands.
yum shell
20. Clean Yum Cache
By default yum keeps all the repository enabled package data in /var/cache/yum/ with each sub-directory, to clean all cached files from enabled repository, you need to run the following command regularly to clean up all the cache and make sure that there is nothing unnecessary space is using. We don’t want to give the output of the below command, because we like to keep cached data as it is.
yum clean allTo view all the past transactions of yum command, just use the following command.
21. View History of Yum
yum history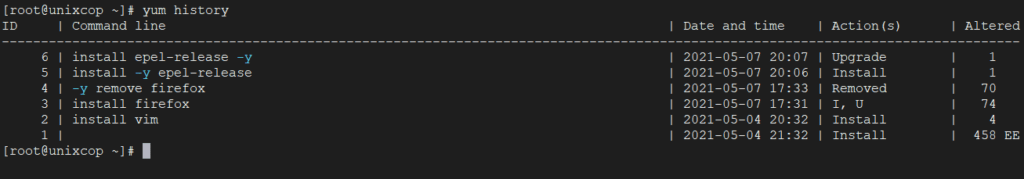
22. Version of Yum
yum --version



