Hello, friends. In this post, you will learn a simple but very useful trick that can help you in Linux administration. Today, you will learn how to change the SSH port.
Is it useful to change the SSH port?
The short answer is yes. In general, something as simple as this can help mitigate attacks against the server or against a specific service.
In addition, it is a good idea to do this so that system administrators have a more personalized reference to the SSH service.
On the other hand, changing the default port adds an extra layer of security to the system. In any case, it is not mandatory to do it, but it is always a good idea to know how to do it for when we have to do it.
Let’s get started.
Change the default SSH port
By default, the SSH port is 22 which can be changed to another port that is available on the firewall.
The SSH service configuration is located in the file named /etc/ssh/sshd/sshd_config which we have to edit with a text editor.
It is recommended that before editing it we make a backup.
sudo cp /etc/ssh/sshd/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.bakThen, you can edit it without worries because if something bad happened, we can restore the initial configuration.
sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd/sshd_configNow locate the line starting with Port 22 and change it to the value of the port you want to assign to SSH. For example:
From
Port 22To
Port 57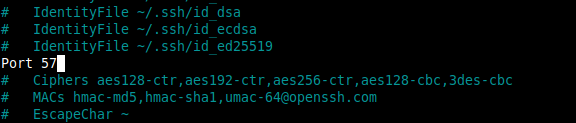
Or any other port you want. Save the changes and close the editor.
Now for the changes to take effect, it is necessary to restart the SSH service.
sudo systemctl restart sshdBe careful because the SSH session will most likely be interrupted.
When you reconnect using SSH, you will have to specify the port as follows:
ssh [user]@[server] -p [port]For example:
ssh [email protected] -p 57Remember that the new port has to be available in the firewall. So, you have to open it.
Conclusion
This little trick that sometimes goes unnoticed can help us to improve SSH administration and customize it more and more.



