This is a continuation of our previous post where we showed you how to install Nagios Server on Ubuntu 20.04. In this post, we focus on how you can add a remote host to the Nagios server. Without much further ado, let’s get on with it.
For demonstration purposes we will deploy a Ubuntu 20.04 host which will be our target system for monitoring.
Step 1: Install Nagios agent and plugins
First, update the package index as follows:
$ sudo apt update
Then install Nagiois NRPE and plugins as shown
$ sudo apt install nagios-nrpe-server nagios-plugins
Great, once installed, proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Configure NRPE agent
Once all the requisite packages have been installed, we need to modify the Nagios NRPE configuration file which is the /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg file.
Open the file and locate the allowed_hosts attribute. By default, this reads as follows.
127.0.0.1,0.0.0.0
Replace the second IP address with the private IP of the Nagios monitoring server. For example.
127.0.0.1, nagios-server-ip
Also, locate the server_address attribute and set it to the remote Linux host that is to be monitored.
server_address=host-ip
Save and be sure to restart the NRPE agent service for the changes to take effect.
$ sudo systemctl restart nagios-nrpe-server
To make sure the NRPE agent is running, verify using the command:
$ sudo systemctl status nagios-nrpe-server
Ensure that the service is running.
Step 3. Add a remote host to Nagios
The last step is to add the remote host to Nagios. So log in to the Nagios server and create a folder where you are going to place the configuration file as follows.
$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers
Then create a configuration file for the remote host as follows. We have named out file ubuntu-host.cfg
$ sudo vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/ubuntu-host.cfg
Add the following configuration. Of course, you need to replace details such as hostname , alias, and address accordingly to match your host’s details.
define host {
use linux-server
host_name hostname
alias My database server
address host-IP-address
max_check_attempts 5
check_period 24x7
notification_interval 30
notification_period 24x7
}
Save and close the configuration file.
Lastly, edit the Nagios NRPE configuration file.
$ sudo vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Uncomment the line below that points to the path of our host’s configuration file
cfg_dir=/usr/local/nagios/etc/servers
Save and close. Then restart Nagios service.
$ sudo systemctl restart nagios.
Nagios listens to TCP port 5666. If UFW is running , you need to open it on both the Nagios server and remote host as follows.
$ sudo ufw allow 5666/tcp
Then reload it to apply changes.
$ sudo ufw reload
And that’s it.
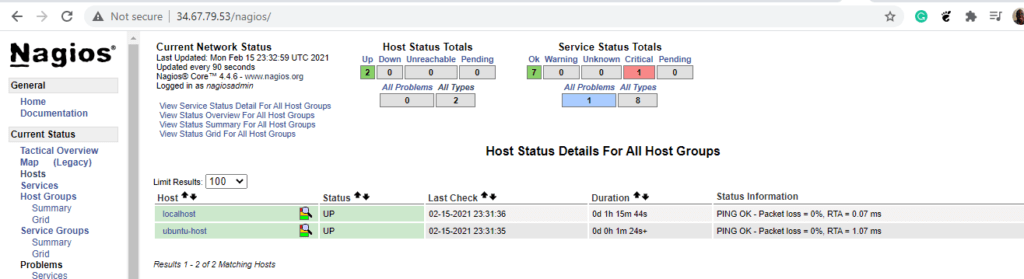
When you visit the Nagios dashboard and click on ‘hosts’ tab on the left pane, your host will be displayed as shown below.