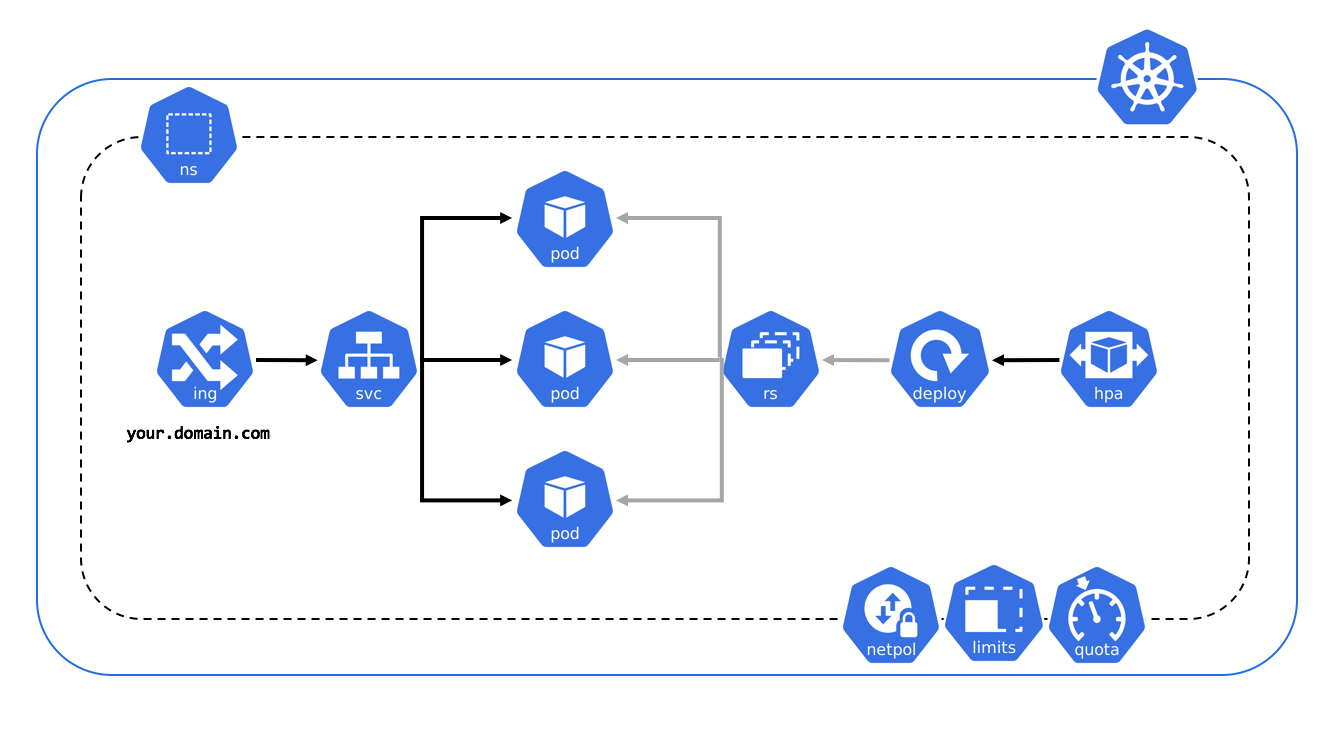
Introduction
Kubernetes is a powerful container orchestration platform that enables developers to manage and deploy containerized applications at scale. In order to take full advantage of Kubernetes’ capabilities, you can deploy a multi-node cluster on Linux. A multi-node cluster allows you to distribute your applications across multiple nodes, ensuring high availability and scalability.
A multi-node cluster is a group of worker nodes working to manage and orchestrate containers.
To deploy a multi-node cluster, you must understand Linux, containerization, and architecture well. You must install and configure various components such as etcd, API server, kubelet, and kubectl. You can deploy the cluster using various tools such as kubeadm, minikube, or kubespray. Once you have deployed the cluster, you can use kubectl to manage and deploy applications on the cluster.
A multi-node cluster provides many benefits, such as increased scalability, reliability, and availability. Distributing containers across multiple worker nodes ensures that your applications are always available and can handle increased traffic loads. It also provides many features such as automated scaling, rolling updates, and load balancing, making managing containerized applications much easier.
This tutorial will walk us through deploying a multi-node Kubernetes cluster on Linux. We will cover the following steps:
- Setting up the environment
- Installing Docker and Kubernetes
- Configuring the cluster
- Joining nodes to the cluster
- Deploying an application
By the end of this tutorial, you will have a fully functional cluster running on Linux that you can use to deploy your applications.
Install Docker:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker.io
Install kubeadm, kubectl, and kubelet:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https curl curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add - echo "deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Disable swap:
sudo swapoff -a sudo sed -i '/ swap / s/^/#/' /etc/fstab
Initialize the master node:
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=192.168.56.0/16 Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster. Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root: kubeadm join <control-plane-host>:<control-plane-port> --token <token> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:<hash>
Set up the Kubernetes network:
kubectl apply -f https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/calico.yaml
configmap/calico-config created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/felixconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamblocks.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/blockaffinities.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamhandles.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamconfigs.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgppeers.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ippools.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/hostendpoints.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/clusterinformations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networkpolicies.c- List all nodes in the cluster:
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION node-1 Ready control-plane,master 4d v1.22.3 node-2 Ready <none> 4d v1.22.3 node-3 Ready <none> 4d v1.22.3
- List all running pods in the cluster:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE kube-system coredns-558bd4d5db-jw6hs 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system coredns-558bd4d5db-x29zk 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system etcd-node-1 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-apiserver-node-1 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-controller-manager-node-1 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-flannel-ds-amd64-5cc7q 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-flannel-ds-amd64-lq8q7 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-flannel-ds-amd64-s8tjf 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-proxy-6mgnz 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-proxy-cwrlf 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-proxy-mbkzh 1/1 Running 0 4d kube-system kube-scheduler-node-1 1/1 Running 0 4d
- Describe a specific pod:
$ kubectl describe pod <pod-name>
Name: nginx-pod
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: node-1/10.0.0.1
Start Time: Mon, 10 Jan 2022 12:00:00 +0000
Labels: app=nginx
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.1.2
IPs:
IP: 10.244.1.2
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://abcdefg1234567890
Image: nginx:latest
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:1234567890abcdef
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Mon, 10 Jan 2022 12:00:01 +0000
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-abcde (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default