mrepo is used for managing repositories from ISO image. It also downloads updates packages from third party repositories. You can also use this utility for network Linux installation. In this article we will learn Linux Repository Management using mrepo.
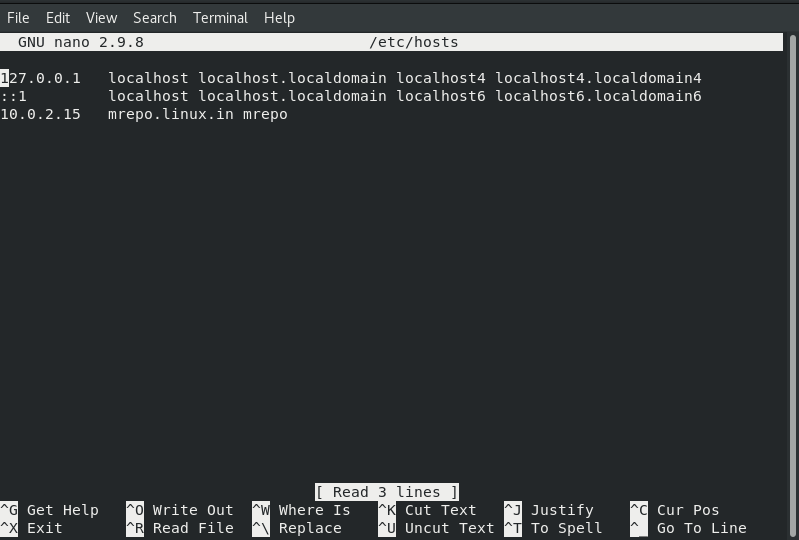
First, Add the IP and name in hosts file.
nano /etc/hostsAdd the following lines:
10.0.2.15 mrepo.linux.in mreposave and close the file.
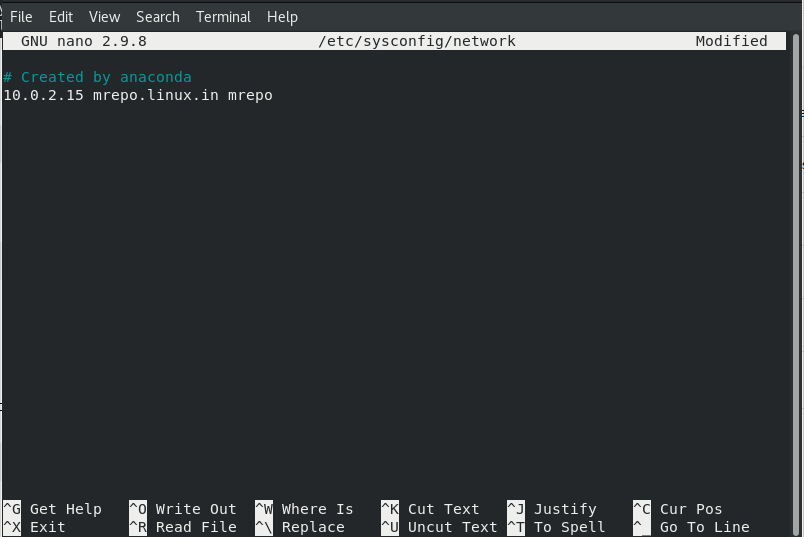
Similarly repeat above step but this time in network configuration file.
nano /etc/sysconfig/networkAdd the following lines:
10.0.2.15 mrepo.linux.in mreposave and exit from the file.
Install the following dependency for mrepo so that we can create repositories as per our need.
yum -y install createrepo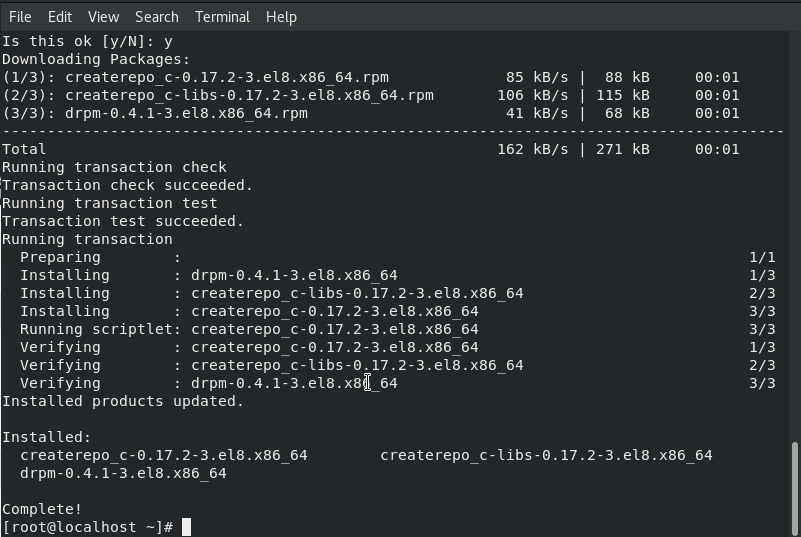
Now Install following packages to support different kinds of mirrors:
yum -y install rsync lftp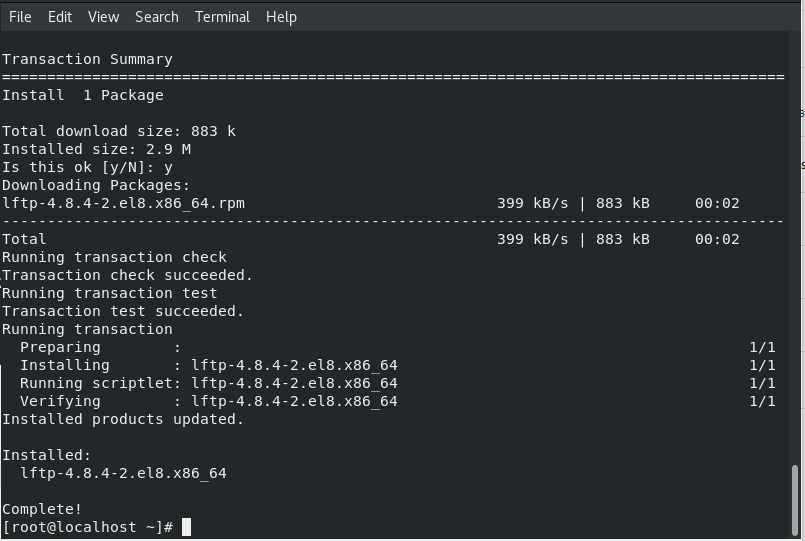
Before the installation of mrepo install EPEL release for CentOS Stream 8.
rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm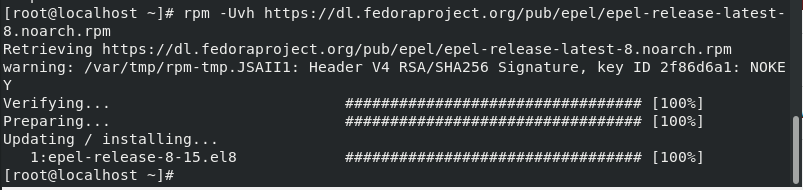
Now, clone the official mrepo installation files from its git repository using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/dagwieers/mrepo.git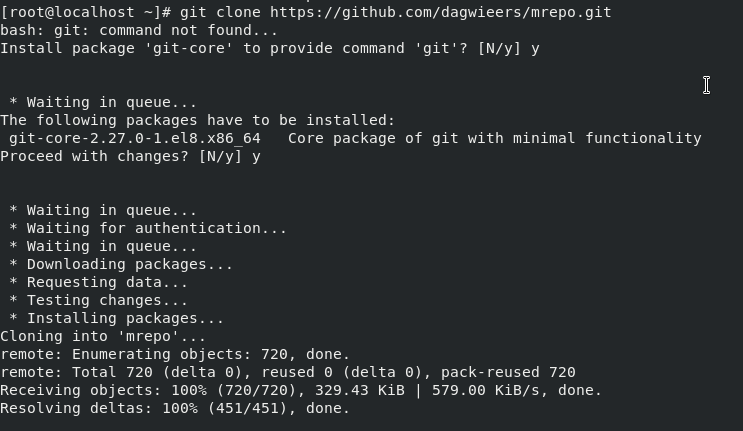
Run the following command to install mrepo:
make install
Now Edit the mrepo configuration file:
nano /etc/mrepo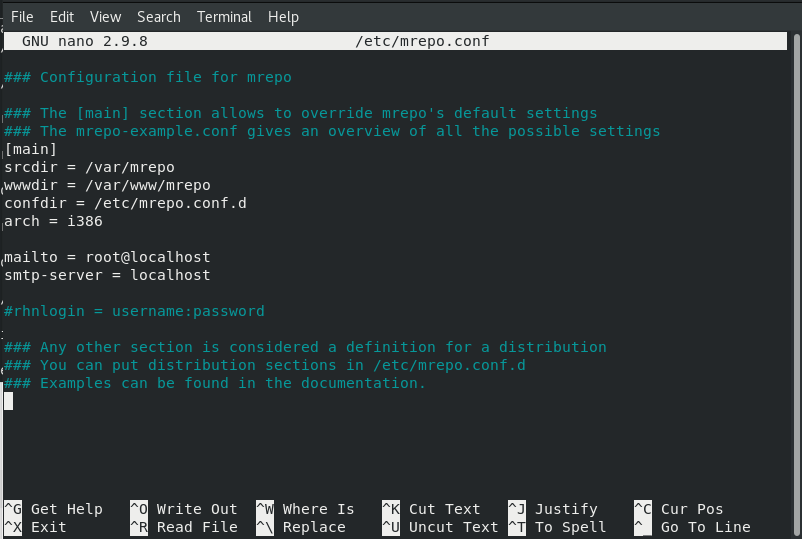
Set the directories as shown in the above image.
Now create a file in /var/mrepo as follows:
mkdir /var/mrepo/puppetserverNow, Create the file under /etc/mrepo.conf.d/
nano /etc/mrepo.conf.d/puppetserverAdd the following lines:
[puppetserver]
name = CentOS Server $release ($arch)
release = 8
arch = x86_64
metadata = repomd yum repoview
### URL
Baseurl = http://yum.puppetlabs.com/el/8/products/x86_64/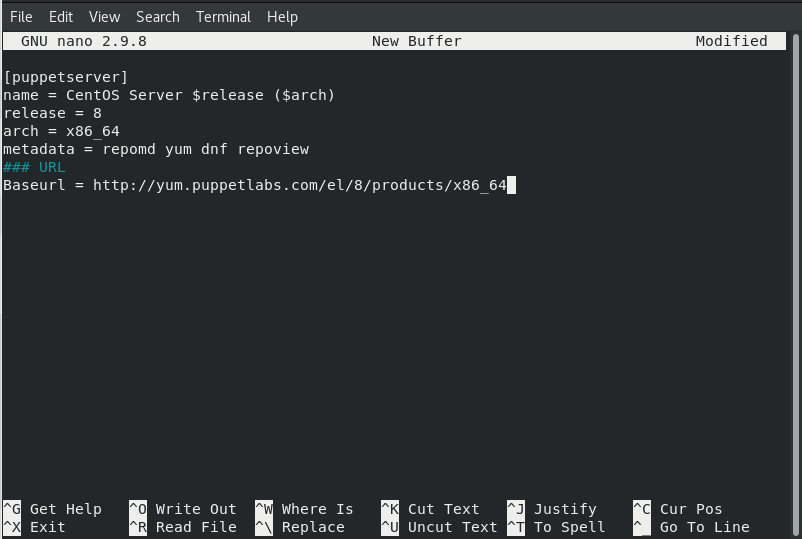
Now start mrepo service using the following command:
service mrepo startRun the following command to update repositories:
mrepo -uvvmrepo installation is now complete you can sue it to create repositories according to your need.



