Although we have touched on the topic of Docker on the site, we have not done it for Fedora. So, in this post, you will learn how to install Docker on Fedora. This post works for both Fedora 38 and Fedora 37.
Introduction
Docker is a software development platform for virtualization with multiple operating systems running on the same host. This is made possible by containers that are distributed as images.
The system is very lightweight because it does not incorporate an operating system, which also allows for better resource utilization. Docker also allows applications to be isolated, which is very useful for testing without bringing down the client’s production server.
Although Docker is a very complex technology, it can be easily controlled through a series of commands.
Unlike virtual machines that can communicate with the host hardware, Docker containers run in an isolated environment on top of the host operating system.
Install Docker on Fedora
First connect via SSH or open a terminal and update the system:
sudo dnf updateNext, install the dnf-plugins-core package which, although it should already be installed, you better be certain.
sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-coreNow add the Docker repository for Fedora
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux /fedora/docker-ce.repoResult:
Adding repo of: https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repoNow you can install Docker on Fedora by running this command:
sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin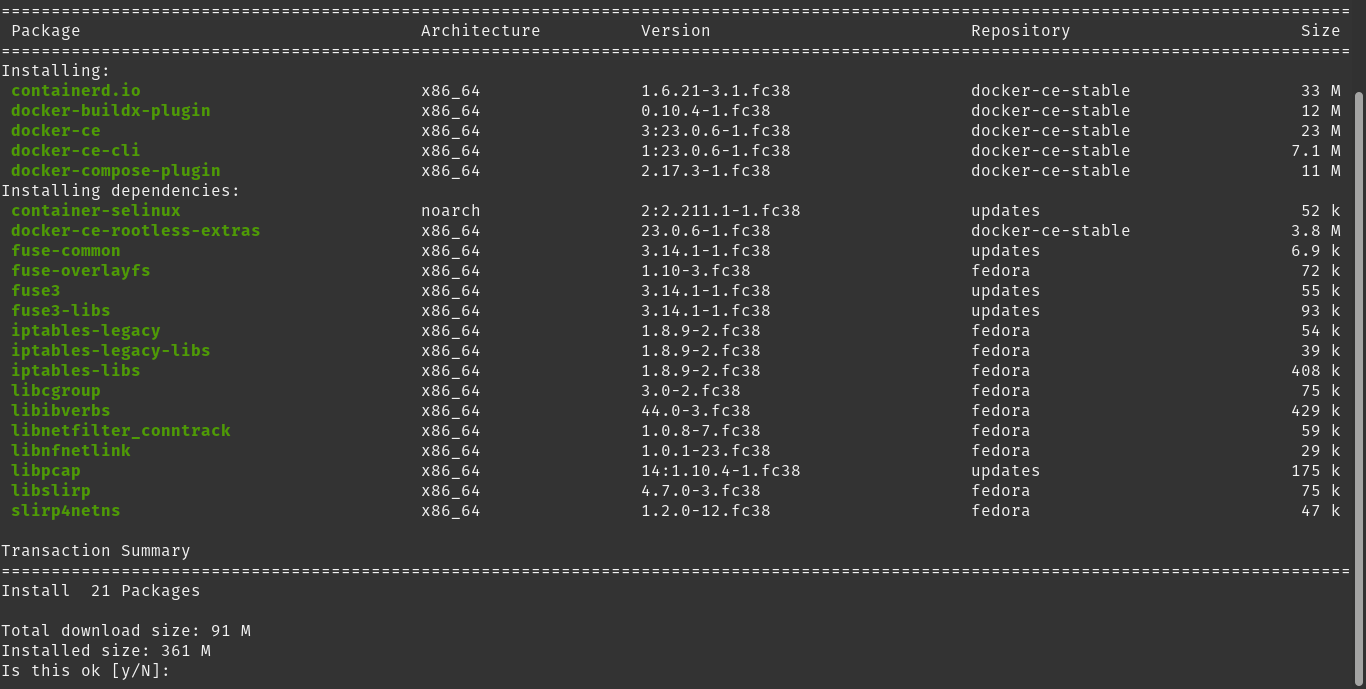
Then, you can check the Docker version with the following command:
docker --versionExample output:
Docker version 23.0.6, build ef23cbc.Starting Docker in Fedora
With Docker installed, you now have to initialize it using systemctl.
sudo systemctl enable --now dockerExample output:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/system/docker.service.The above command not only starts the Docker service, but also enables it to start with the system. It’s that quick and easy.
The next thing to do is to check the status of the service to make sure everything is OK.
sudo systemctl status docker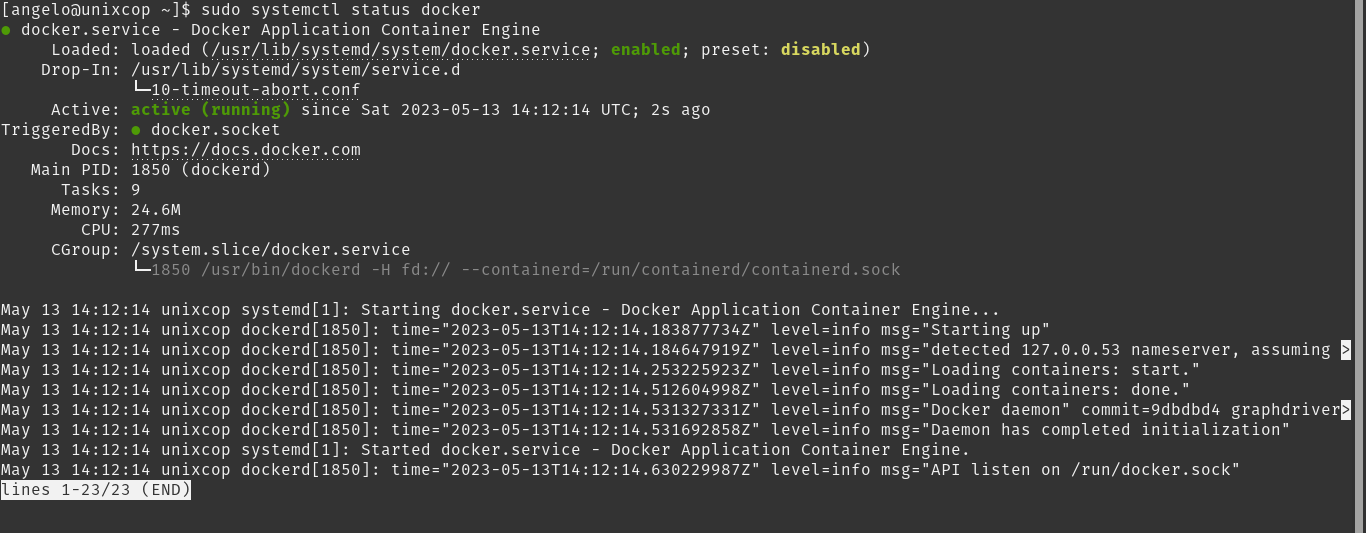
With that, we know that Docker is running without problems.
Testing Docker after the installation
By default, Docker requires root to run, but this is not a good practice to follow. So modify your user to add this user to the docker group.
sudo usermod -aG docker angeloThen, you can run the test image
docker run hello-worldIf all goes well, you will see something like this
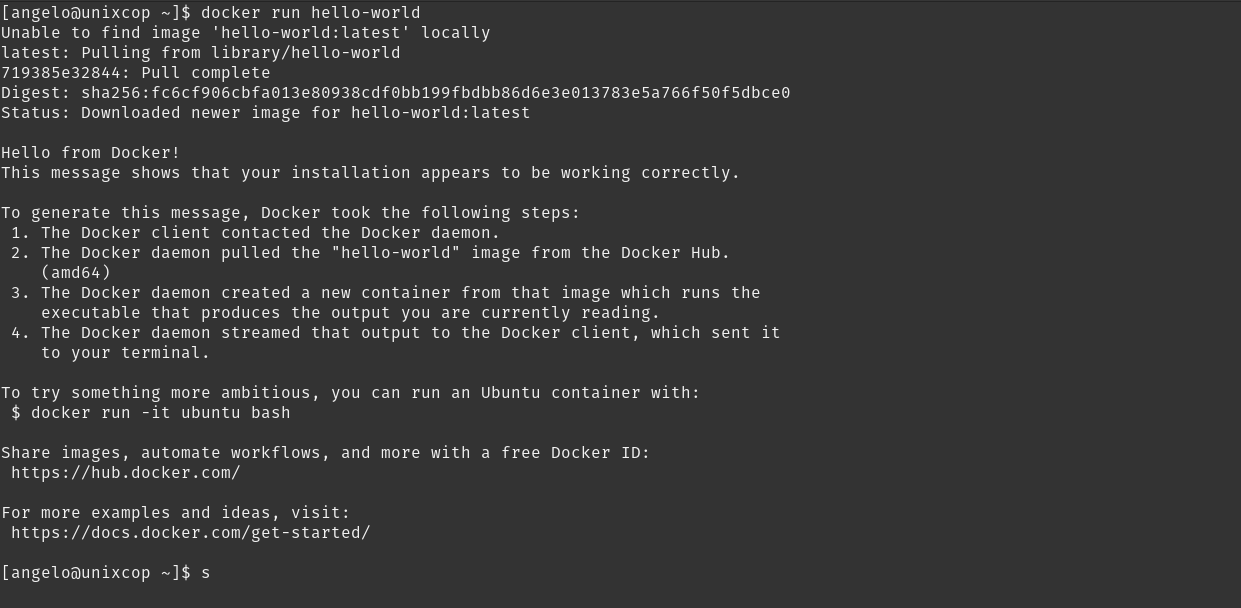
Conclusion
In this post, you learned how to install it on Fedora by doing a simple and fast process.



