What is Dig?
Dig (Domain Information Groper) is a command-line utility that performs DNS lookup by querying name servers and displaying the result to you. The Dig command is another powerful tool similar to nslookup for diagnosing DNS-related problems.
In this tutorial, we’ll see all the primary uses of the dig command with practical examples in the Linux operating system.
Install Dig on system
Ubuntu/Debian
apt-get install dnsutils
RHEL/Centos
yum install bind-utilsVerify Installdig -v
Command Syntax
Before start command execute, let’s see how Dig command works. The Dig command syntax used as below:
dig server name type
Where server represents Name or IP address of the name server to query. It can be an IPv4 address or an IPv6 address in colon-delimited notation. The dig command sent queries to the /etc/resolv.conf file and the name servers listed there. The reply from the name server that responds is displayed.
The Name represents the server’s DNS to query & the Type indicates what Type of query is required, such as A, MX, SIG, etc.
Now let’s see some practical examples with dig command
Basic Command and Output (DNS Lookup)
dig unixcop.com
this is very basic command line parameters to see dns address information.

The result ANSWER SECTION: contains the preliminary information you have requested. You can ignore other parts of the output which have additional details about the query you made. Generally, dig looks for the “A” record of the domain specified, but you can specify other records also. The MX or Mail exchange record tells mail servers how to route the email for the domain. Likewise, TTL, SOA, etc.
MX Record Lookup.
dig google.com mx

Check Short & Details information.
dig unixcop.com +short
dig unixcop.com +noall +answer
NS Record Lookup.
dig unixcop.com ns

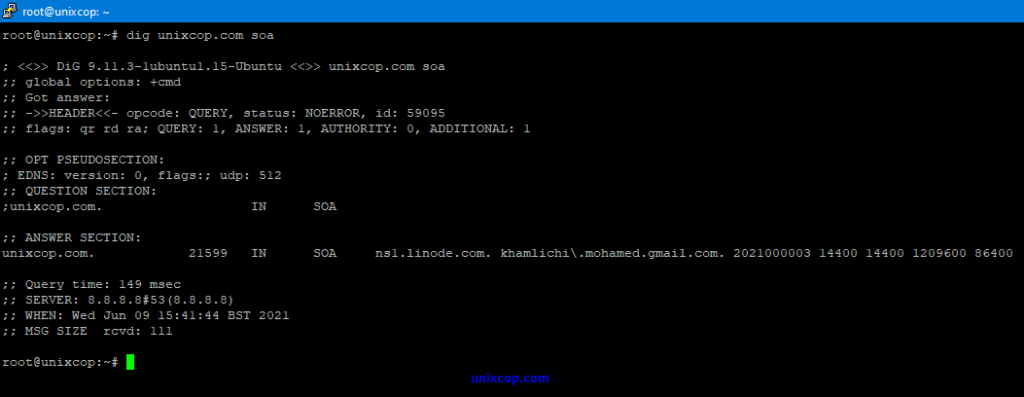
Lookup SOA record.
dig unixcop.com ns
Reverse DNS(rDNS) Lookup.
dig -x 104.237.129.44

Lookup TTL Record.
dig unixcop.com ttl

Lookup ANY DNS Records.
dig unixcop.com any
dig unixcop.com any +noall +answer
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we tried to find out the maximum usage of dig command which may help you search (DNS) Domain Name Service-related information. Share your thoughts through the comment box. you can follow my other posts.



