Hello, friends. You will learn in this post how to generate SHA-256 Hash on Linux using the terminal. This although simple allows you to compress and sign files for later verification.
SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and first published in 2001.
This tool has many security variants, but one of the most widespread is SHA256, which is the one we will use in this post.
So, what is the purpose of this post? Well, to generate checksums to a file that allows with this, to check the integrity of the file. One of the obvious reasons is to maintain a high standard of security in the transmission of files.
On Linux, we have the command sha256sum with which you can take advantage of the protocol.
Generate SHA-256 Hash on Linux using the terminal
The first thing to say is that the sha256sum command is built into the system by default. So, you don’t need to install anything.
Open a terminal and, for example, add some text to a .txt file, remember it can be any type of file.
echo "Welcome to Unixcop" > sample.txtNow create the SHA256 hash for the file with this command
sha256sum sample.txt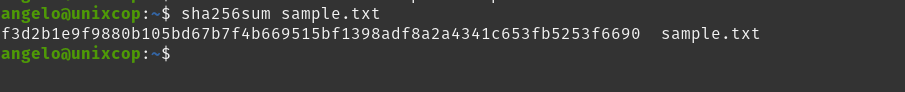
Generating a screen output like this
f3d2b1e9f9880b105bd67b7f4b669515bf1398adf8a2a4341c653fb5253f6690 sample.txtAs you can see, the structure is simple. The first 65 characters refer to the hash itself. Then, a blank space and the file path.
Note that sha256sum has two modes, binary and text. In the case of binary, you will see a * in the output. However, for the most basic tasks, both options are valid.
As you can see, in this case, you have worked with a file that is in the same directory as the prompt, but it may be somewhere else. You may even want to store the output in another file for later verification.
sha256sum /path/to/file.txt > [output-file]For example,
sha256sum /home/angelo/sample.txt > checkAnd then, you can check it
sha256sum --check checkAnd you will have a screen output like this
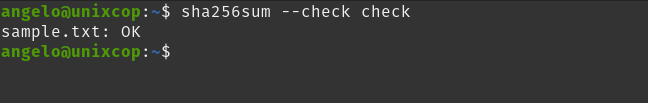
That is, the file is complete and has not been changed. But if it has, see what happens.
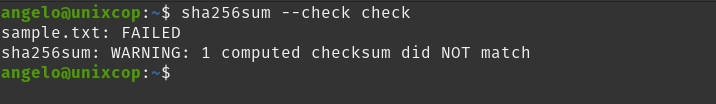
As you can see, the importance of checksums is that they allow to know if a file was or was not modified in the transmission.
Conclusion
In this post, you learned something as simple as important about checksums on Linux. So now you have to apply it in your work or situations.



