In this guide, we will illustrate how to change current runlevel with two methods.
Introduction
A runlevel is a mode of operation in the computer operating systems that implements Unix System V-style initialization. Conventionally, seven runlevels exist, numbered from zero to six. S is sometimes used as a synonym for one of the levels. Only one runlevel is executed on startup; run levels are not executed one after another (i.e. only runlevel 2, 3, or 4 is executed, not more of them sequentially or in any other order).
runlevel defines the state of the machine after boot. Different runlevels are typically assigned (not necessarily in any particular order) to the single-user mode, multi-user mode without network services started, multi-user mode with network services started, system shutdown, and system reboot system states.
The exact setup of these configurations varies between operating systems and Linux distributions. For example, runlevel 4 might be a multi-user GUI no-server configuration on one distribution, and nothing on another. Runlevels commonly follow the general patterns described in this article; however, some distributions employ certain specific configurations.
Runlevel
The default runlevel can be set either by using the systemctl command or making a symbolic link of runlevel targets to the default.target file.
Change Runlevel using systemctl Command
- Check the current run level.
systemctl get-default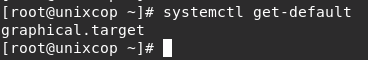
The system’s current default runlevel is graphical.target (runlevel 5).
- To change the default runlevel to runlevel 3 (multi-user.target), run the following command.
systemctl set-default multi-user.target- Reboot then check it out.
reboot- Check again that the default current runlevel is runlevel 3 (multi-user.target).
systemctl get-default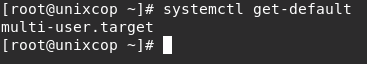
Change Runlevel using symbolic Link for target
- Check the current runlevel.
systemctl get-default
- List out the runlevel files in the systemd directory.
ls -l /lib/systemd/system/runlevel*target 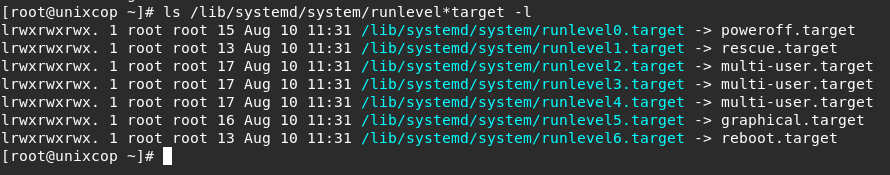
The default runlevel is multi-user.target (runlevel 3).
- Make a symbolic link of runlevel5.target to the default.target file.
ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/runlevel5.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target
OR
ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/graphical.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target- Reboot then check again
reboot- Verify that the default runlevel is runlevel 5 (graphical.target) post the reboot.
systemctl get-default
NOTE: You can switch the current runlevel with the systemctl isolate [target] command in the session.
systemctl isolate graphical.target
OR
systemctl isolate multi-user.targetAvailable Targets / Runlevels
| Runlevel | Target Units | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | runlevel0.target / poweroff.target | Power off the system. |
| 1 | runlevel1.target / rescue.target | Single User mode |
| 2 | runlevel2.target / multi-user.target | multi-user mode. |
| 3 | runlevel3.target / multi-user.target | multi-user mode. |
| 4 | runlevel4.target / multi-user.target | multi-user mode. |
| 5 | runlevel5.target / graphical.target | Graphical mode. |
| 6 | runlevel6.target / reboot.target | Reboot the system. |
Conclusion
That’s it, we showed you how to change the runlevel with two methods in rhel and centos 8.
thank you



