Hello, friends. Talking to some friends who have just installed Linux, I noticed how something as simple as changing the screen resolution can be a bit complicated to do. So in this post you will learn how to do it both from the graphical interface and from the terminal.
Many newbies come to Linux and specifically Ubuntu a bit lost. However, with the passage of time, they understand that it is even easier and more intuitive than other systems. But not only that, it is also quite flexible. So, you can change the screen resolution both through the graphical interface and from the terminal.
How to change the screen resolution in Ubuntu 22.04 / 20.04
Method 1: using the graphical user interface
Usually, the novice dislikes the terminal, so we will start with the graphical interface, which is GNOME. This modern writing environment has all the necessary options, so you won’t miss anything.
First, open the main menu and type Settings. Then access the system options.
Now go to the Displays section and in it, you will see the Resolution value.
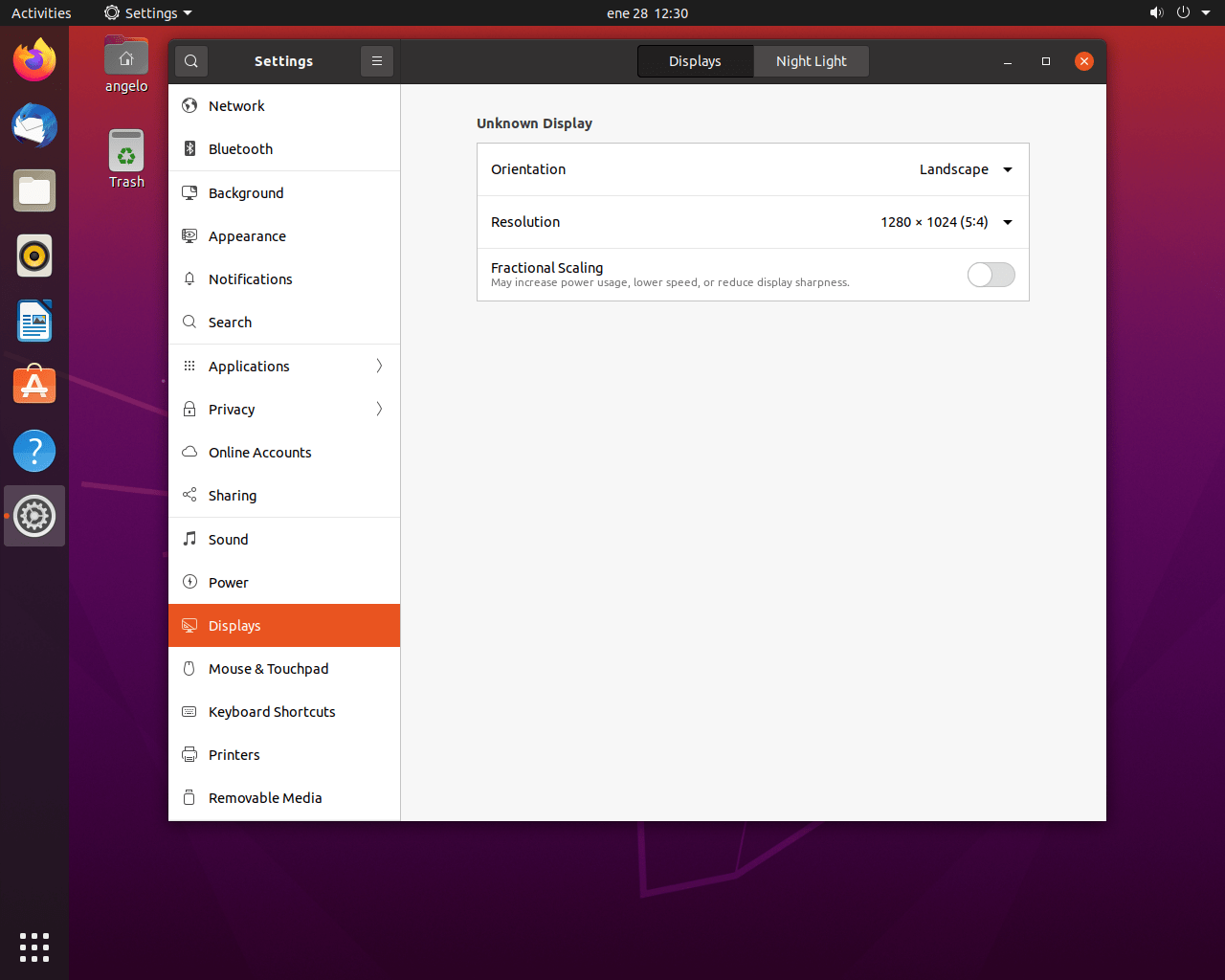
From the dropdown list, you will see the resolutions compatible with your screen. This will also vary depending on the graphics card and driver installed. So, if the appropriate screen resolution is not shown, it is because of a driver or compatibility issue.
Now you just need to select the resolution you want.
If you are satisfied, keep the changes and that’s it.
Method 2: Change the screen resolution using the terminal
Yes, you can also do this process using the terminal. It is simple thanks to the xrandr tool. With this tool, you can quickly configure the screen.
This may not seem useful to beginners, but in the future it can be useful in configuration scripts or other situations.
By default, this package is installed in Ubuntu 22.04, so you don’t have to do much.
Open a terminal from the main menu and run
xrandrYou will get an output screen like this
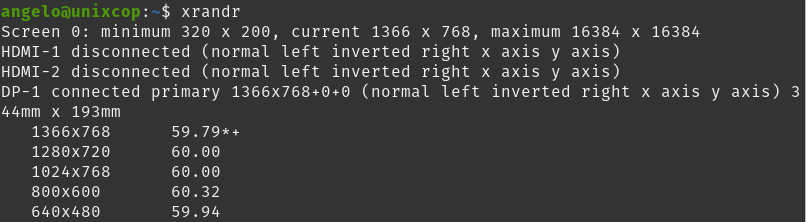
There you will have important information about the monitor configuration. In this case, it shows the minimum allowed resolution, the current resolution and the maximum allowed resolution.
You will also see information about ports and supported screen resolutions.
Note that in this display output, the monitor alias is DP-1. You will recognize it quickly because it says connected and shows the active resolution.
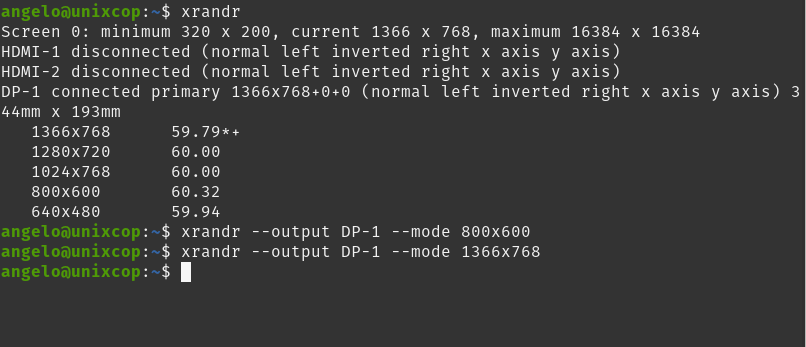
To change the resolution on the main monitor, you can run this syntax
xrandr --output [monitor-alias] --mode [resolution]For example,
xrandr --output DP-1 --mode 800x600And the changes will be automatic.
Conclusion
It was a short post, but with it, you learned how to change the screen resolution on Ubuntu using both the GUI and the terminal. I hope you liked it.



