Hello, friends. In this post, you will learn how to install nmap on Fedora 36. Besides that, we will take a look at the basic operation of this tool.
What is nmap?
According to the nmap website:
Nmap (“Network Mapper”) is a free and open source utility for network discovery and security auditing. Many systems and network administrators also find it useful for tasks such as network inventory, managing service upgrade schedules, and monitoring host or service uptime.
With nmap we can:
- Scan the network and its nodes.
- Identify open ports on a target computer.
- Determine what services are running on the target computer.
- Obtain some characteristics of the network hardware of the target machine.
Nmap runs on all major computer operating systems, and official binary packages are available for Linux, Windows, and macOS. This means that we can confidently install it on our favorite system and then start mapping.
So let’s get started.
Install nmap on Fedora 36
Fortunately, namp is in the official Fedora 36 repositories. So, we just have to open a terminal and update the system
sudo dnf updateNow, we just need to install nmap on the system with the following command
sudo dnf install nmap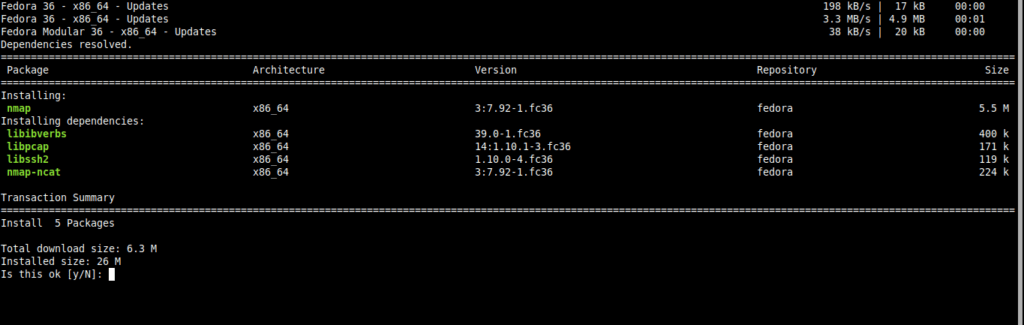
Then, you have to verify the installed version:
nmap --version
Nmap version 7.92 ( https://nmap.org )
Platform: x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu
Compiled with: nmap-liblua-5.3.5 openssl-3.0.5 libssh2-1.10.0 libz-1.2.11 libpcre-8.45 libpcap-1.10.1 nmap-libdnet-1.12 ipv6
Compiled without:
Available nsock engines: epoll poll selectNow you just need to use it.
Basic use of nmap on Fedora 36
The first thing I advise you to do is to take a look at the help provided by the command.
nmap -hThis way you will have a basic reference on how to use it.
If you want to do a scan of a specific host, you have to run
nmap domain.comOr directly using the host’s IP address
nmap 192.168.1.100You will get an output screen similar to this:
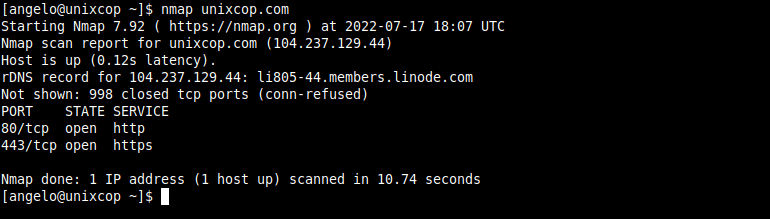
You can also scan a range of addresses. For example:
nmap 192.168.1.100-20Or even the entire network:
nmap 192.168.1.0/24If you want a more complete scan and screen output, you can add the -vvv option
nmap -vv [host]Or you can specify the port you want to check
nmap -vv -p 1000 [host]In this case, I have chosen port 1000 but it can be any port.
Conclusion
nmap is an excellent tool that allows us to scan networks and ports. Now you know how to install it on Fedora 36.



