Hello, friends. In a recent post, we explained how to install ArangoDB on CentOS and derivatives. Today we will install ArangoDB on Debian 11 which is a widely used system for these purposes.
As we have explained before, ArangoDB is a NoSQL database manager focused on scalability and easy administration. It has a free community version and a paid version that allows us to get more features and professional support.
Like many, it is based on documents and collections for data storage, so it is common to find it in mobile applications or configuration scripts.
Let’s get to it.
Preparing the system for installation.
Before we start with the installation, we need to update the system
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgradeThereafter, we need to install some necessary packages.
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https gnupg curlAnd now we can continue.
Installing ArangoDB on Debian 11
We can do the installation manually, by downloading the corresponding binaries. But we can also add the ArangoDB repository for Debian 11 to ease the process but also gain integration with the system.
To achieve this, download the GPG key of the repository.
curl -OL https://download.arangodb.com/arangodb39/DEBIAN/Release.keyThen, add it to the system
sudo apt-key add - < Release.keyThereafter, add the repository to the system by running
echo 'deb https://download.arangodb.com/arangodb39/DEBIAN/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/arangodb.listRefresh APT so that it downloads package information to the repository
sudo apt updateNow install ArangoDB using the command
sudo apt install arangodb3=3.9.1-1In the installation process, you will be able to set the root password for ArangoDB. Then you will have to confirm it.
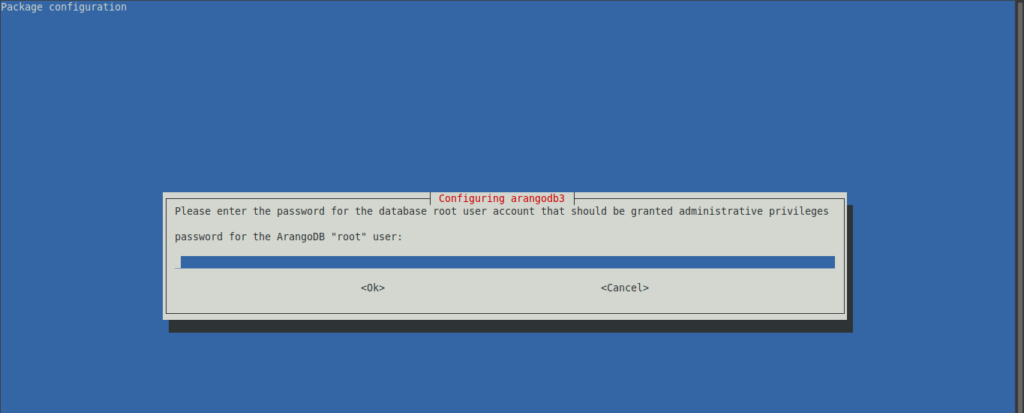
Then you will have to define if you want the databases to be updated automatically.
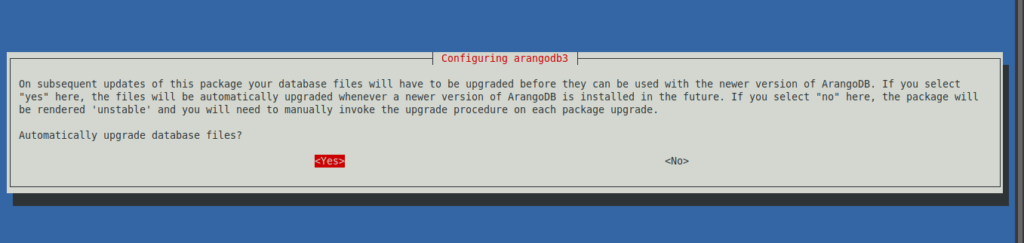
If you choose yes, then you have to enable the backup and the installation will continue as normal.
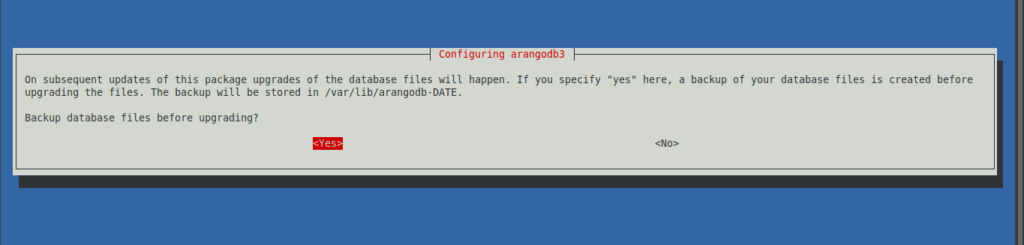
Next, check the status of the service to see if ArangoDB has been installed on the system.
sudo systecmtl status arangodb3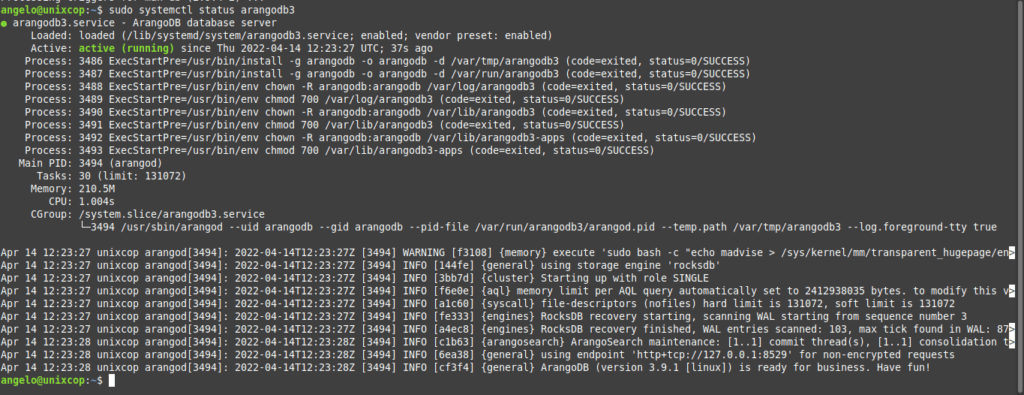
Next, you can log in to the console by running
arangoshOptional: Configuring the ArangoDB web interface
One of the main features of ArangoDB is that it has a powerful web interface where you can do all the operations you want quickly. It comes by default to work on http://127.0.0.1:8529. This is fine if you have installed it on your personal computer, but if you have installed it on a server, then you have to enable access to the other hosts.
To achieve this, go to the ArangoDB configuration file
sudo nano /etc/arangodb3/arangod.confAnd at the beginning of the file, check the line
endpoint = tcp://127.0.0.1:8529And replace it with this one
endpoint = tcp://0.0.0.0.0:8529Save the changes and close the editor. To apply the changes, restart the service.
sudo systemctl restart arangodb3Remember to open port 8529 in the firewall.
Now open your web browser and go to http://your-server:8529 and you will see the login screen.

Then, enter your credentials
If all goes well, you will be able to choose the collection you want to connect to.

And finally, you will see the ArangoDB interface.
Conclusion
In this post, you learned how to install ArangoDB on Debian 11. We are talking about an excellent and professionally supported NoSQL database manager.



