SSHGuard is an open-source daemon that shields hosts from brute-force attacks. It accomplishes this through monitoring and aggregation of system logs, detecting attacks, and blocking attackers using one of the Linux firewall backends: iptables, FirewallD, pf, and ipfw.
Initially designed to provide an extra layer of protection for the OpenSSH service, SSHGuard also protects a wide range of services such as Vsftpd and Postfix. It recognizes several log formats including Syslog, Syslog-ng, and raw log files.
SSHGuard is quite similar to Fail2ban only that it is written in C (Fail2ban is written in Python), is lighter, and provides fewer features.
In this guide, we will demonstrate how you can install and configure SSHGuard to block SSH brute force attacks in your Linux server.
Step 1: Install SSHGuard on Linux
We start off with the installation of SSHGuard on Linux.
Install SSHGuard on Debian/Ubuntu
First, update the package lists and then install SSHGuard from the default repositories using the apt package manager.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install sshguardOnce installed, the SSHGuard service starts automatically, and you can verify this using the command:
$ sudo systemctl status sshguard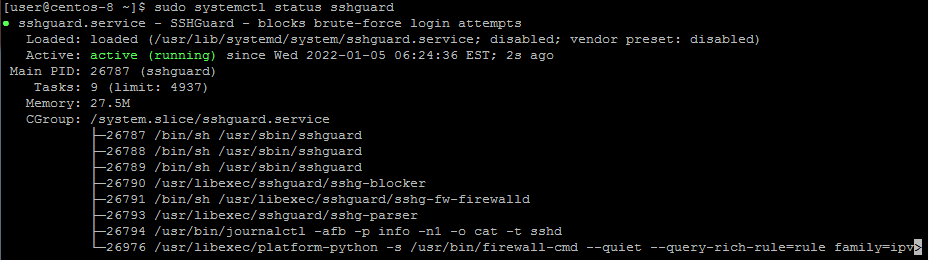
Install SSHGuard on Yum/RHEL Systems
For RHEL-based distributions such as CentOS, start off by installing the EPEL repository as provided in the command below.
$ sudo yum install epel-releaseOR
$ sudo dnf install epel-releaseWith EPEL in place, go ahead and install SSHGuard using the dnf package manager.
$ sudo dnf install sshguardOnce installed, start and set SSHGuard to start on system startup or reboot.
$ sudo systemctl start sshguard
$ sudo systemctl enable sshguardBe sure to verify that SSHGuard is running as expected.
$ sudo systemctl status sshguard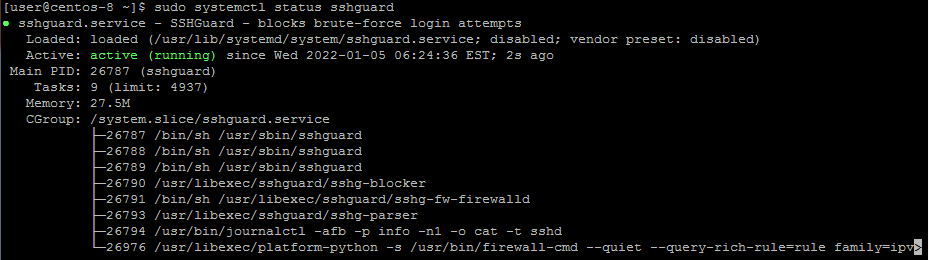
Step 2: SSHGuard Configuration on Linux
SSHGuard actively monitors the /var/log/auth.log, /var/log/secure systemd journal, and syslog-ng log files for failed login attempts.
For each unsuccessful login attempt, the remote host is banned for a limited amount of time which, by default is set at 120 seconds. Thereafter, the ban time goes up by a factor of 1.5 with each successive failed login attempt.
The time the offending hosts are banned, in addition to other parameters is specified in the sshguard.conf file. You can access the configuration file using the vim editor as shown.
$ sudo vim /etc/sshguard/sshguard.confOn RHEL-based distributions, the config file is located in the following path.
$ sudo vim /etc/sshguard.confHere is a sample of the configuration file when viewed from Ubuntu / Debian.
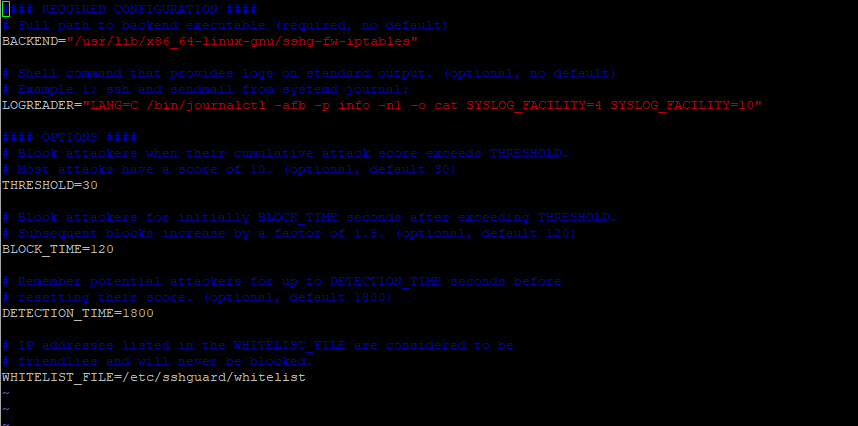
Focusing on the main options:
- The BACKEND directive points to the full path of the backend executable. In this example, we see that IPtables is set as the default firewall backend.
- The THRESHOLD directive blocks attackers when their attack score exceeds the specified value.
- The BLOCK_TIME option is the number of seconds that an attacker is blocked after every successive failed login attempt. By default, this is set to 120 after the first attempt. This increases with each successive failed login attempt.
- The DETECTION_TIME option refers to the time in seconds during which the attacker is registered or remembered by the system before their score is reset.
- The WHITELIST_file option point to the full path of the whitelist file that contains hosts which are not supposed to be blacklisted.
Step 3: Configure SSHGuard to Block SSH Brute Force Attacks
To ward off brute-force attacks, you need to configure on the following firewalls to work with sshguard.
Block SSH Attacks Using UFW
If you have UFW installed and enabled on your Ubuntu / Debian system, modify the /etc/ufw/before.rules file.
$ sudo vim etc/ufw/before.rules
$ sudo vim etc/ufw/before.rulesAdd the following lines just after the “allow all on loopback” section.
# allow all on loopback
-A ufw-before-input -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A ufw-before-output -o lo -j ACCEPT
# hand off control for sshd to sshguard
:sshguard - [0:0]
-A ufw-before-input -p tcp --dport 22 -j sshguardSave the file and restart UFW.
$ sudo systemctl restart ufwNow attempt logging into the server from a different system with the wrong credentials and notice that you will be locked out for 120 seconds after the first failed login attempt.
You can verify this by checking the auth.log log file.
$ sudo tail -f /var/log/auth.log
After the next failed log attempt, the block time increases to 240 seconds, then 480 seconds, then 960 seconds, and so on.
Block SSH Attacks Using Firewalld
If you are running firewalld, ensure that it is set up and enabled. Then execute the following command to enable sshguard on your preferred zone.
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-rich-rule="rule source ipset=sshguard4 drop"To apply the changes, reload Firewalld and sshguard.
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
$ sudo systemctl restart sshguardThen verify the rule as follows:
$ sudo firewall-cmd —-info-ipset=sshguard4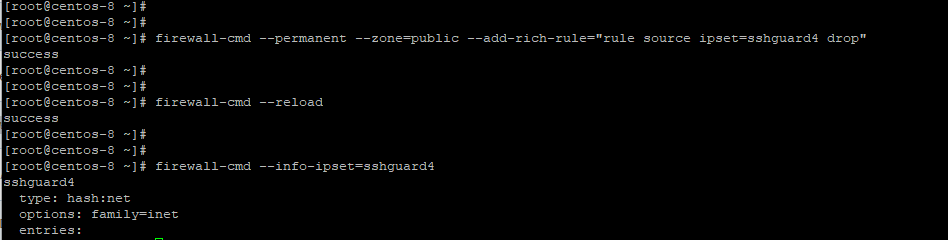
Block SSH Attacks Using Iptables
If you are still using Iptables, first, create a new chain rule for sshguard in Iptables to start blocking unwanted guests.
# iptables -N sshguardNext, update the INPUT chain to direct traffic to sshguard and block all traffic from nefarious parties.
# iptables -A INPUT -j sshguardTo block specific ports such as SSH, POP, and IMAP from abusers run the command:
# iptables -A INPUT -m multiport -p tcp --destination-ports 22,110,143 -j sshguardAnd finally, save the rule for the changes to come into effect.
# iptables-save > /etc/iptables/iptables.rulesStep 4: How to Whitelist SSH Blocked Hosts
To whitelist a blocked host, simply specify its hostname or IP address in the whitelist file which is located in:
/etc/sshguard/whitelist - Ubuntu/Debian
/etc/sshguard.whitelist - RHEL-based distrosAfterwards, be sure to restart the sshguard daemon and the firewall backend for the changes to apply.
In this guide, we demonstrated how you can block SSH Bruteforce attacks using SSHGuard on Linux systems.
Please refer to our homepage for further guides.



